Feb. 2024 climate extremes: Welcome to 2024 as we race down the road to Hothouse Earth
Rev. 0 – 11/03/2024!
2023 set new planetary extremes as our activities force global temperatures ever higher on the way to mass extinction. 2024 looks even worse! Soon humans will no longer be able to survive in the climate we are forging.
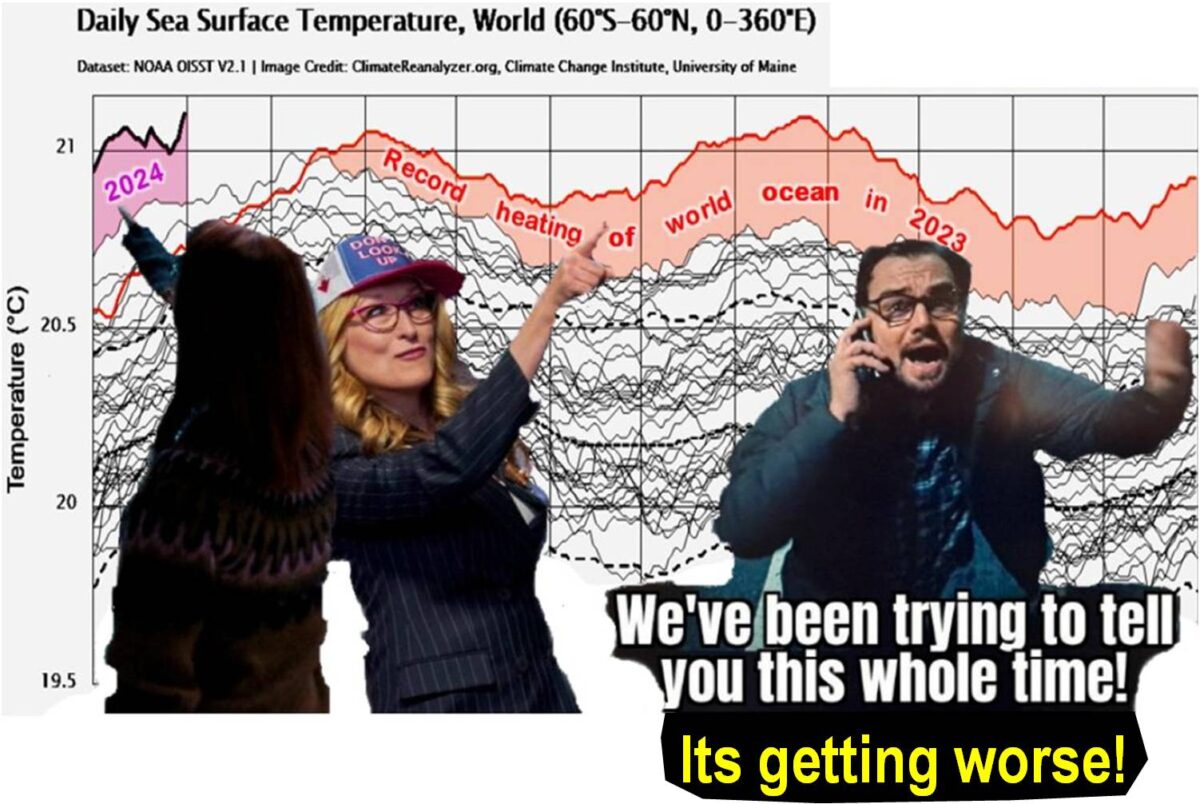
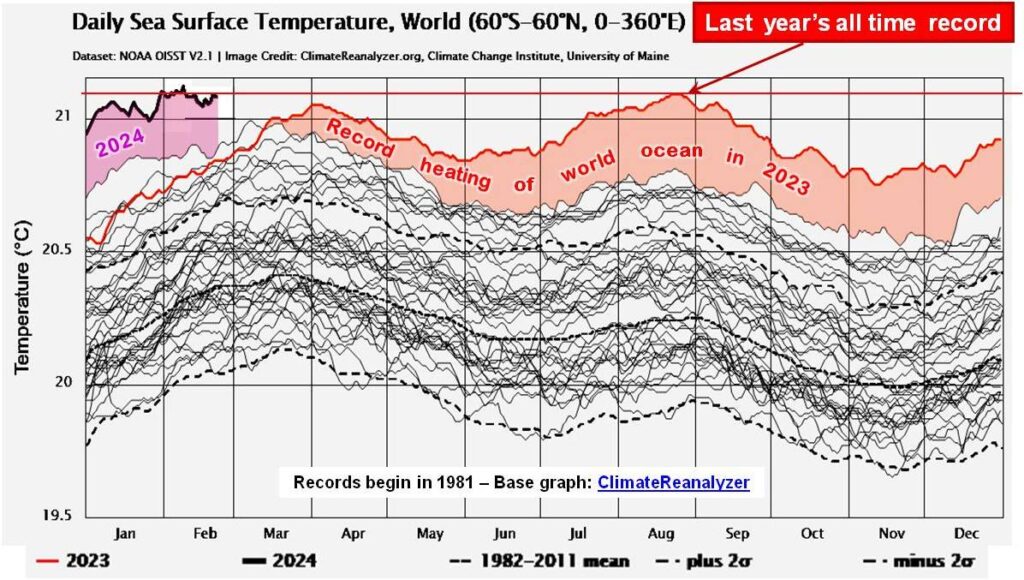
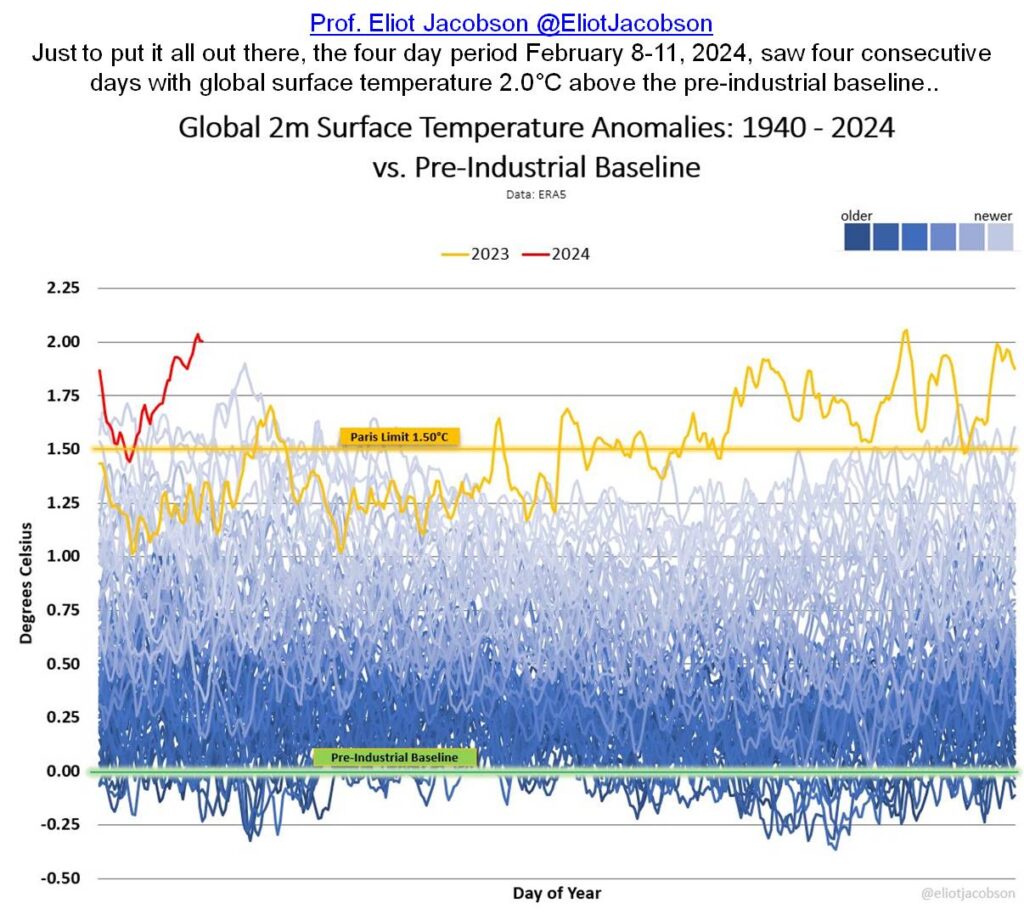
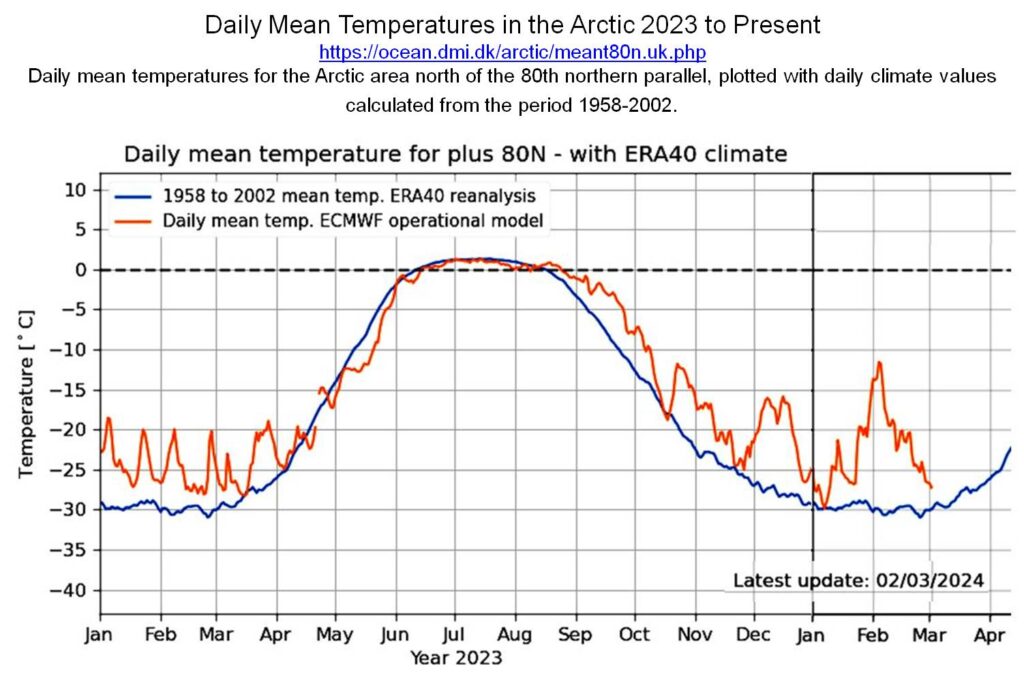
My featured image of the state of Earth’s oceans up to February 1 is already dated (see below). The world’s sea surface temperature is still rising and setting new records every day since 14 March last year and is within 4 days of overlapping last years’ unbroken sequence of record days. ClimateReanalyzer – updated daily – shows global average Sea Surface Temperatures for every day since Sept 1, 1981. (This web page also provides links to details on the methodologies used to compute these values.)
The implications of these observations is truly alarming when placed in the context of Earth’s climate system. Emergency mobilization of global action is required if we are to have any hope of avoiding the existential consequences of runaway warming that may have actually started. This level of action will require many individual sacrifices that governments and people prefer not to think about and will be reluctant to make. However, history shows (e.g., mobilization for WWII)1 that humans can and will unite and act if the reality of the threat is accepted and taken seriously.

What follows is no hoax! It is how universal physical laws work in the real world of our planet. Ignore the evidence at your peril, or accept reality and work to survive the impending apocalypse foretold. As will be explained, my featured image announces the existential threat all humanity faces from global warming – currently being largely ignored by politicians, press, and citizens.
March 13, 2024, when this year’s continuous all-time record heating builds on top of last year’s continuous-all time record heating, should be taken as our “Pearl Harbor Day“.
Hot oceans drive many potentially catastrophic changes to planetary climate.

Earth’s accelerating energy imbalance
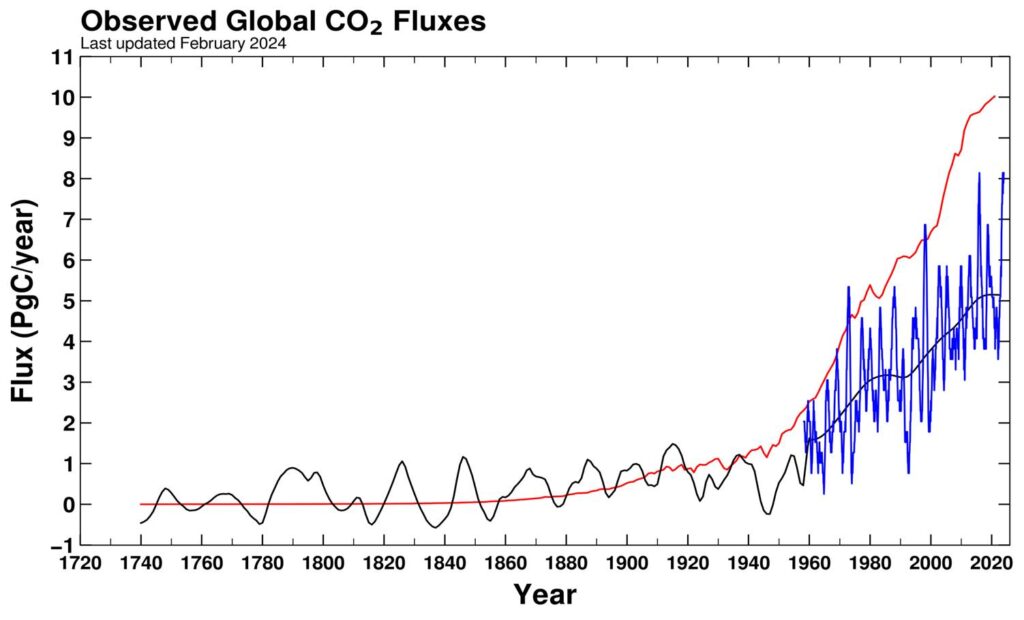
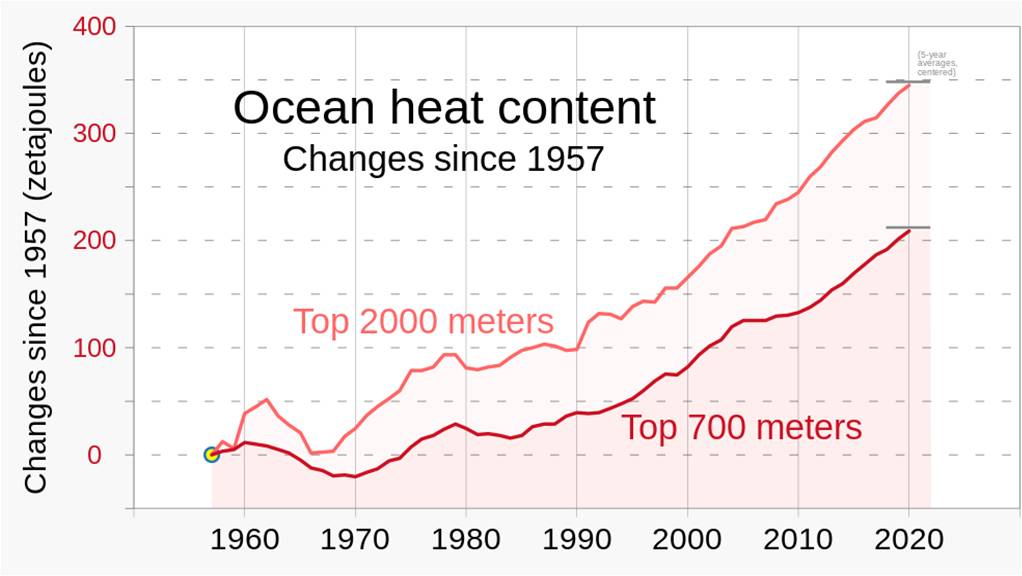
Earth oceans are warming at a geologically prodigious rate that we can clearly see major changes in a human lifetime (Figure 1). This is because oceans are being flooded with excess energy much faster than they can lose it. The rising temperature has dire consequences. However, before presenting the consequences of ocean warming, we should understand what is causing the warming.
The average surface temperature of our planet (i.e., the biosphere) is determined by balance between the amount of (heat) energy it receives from all sources versus the amount of energy it loses to outer space as radiant heat.
The vast amount of energy received by the biosphere comes directly from the Sun, as “radiant energy“, mainly in the form of visible light. This varies only slightly over time, due to astronomical factors. There are also two very minor internal sources (“internal energy“) left over from Earth’s formation billions of years ago that I mention for completeness: (1) the decay of radioactive elements in the Earth’s body and (2) the residue heat from the conversion of gravitational potential energy into heat as our planet formed by condensation of small part of the solar nebula that also gave birth to the Sun. This internal energy, brought to the surface from below by conduction and volcanic activity, accounts for only about 0.03% of the total energy warming the surface.
Given that vacuums cannot conduct heat, and that gravity stops particles from carrying away energy (i.e., convection), the only way Earth can lose heat is by radiation. All objects warmer than absolute zero, including Earth, lose heat by “black-body” radiation. Objects close to absolute zero lose energy via microwave radiation. As the object’s temperature rises heat energy is able to escape at shorter (more energetic) wavelengths – with a growing percentage of energy at these shorter wavelengths. E.g., hot iron may be ‘red hot’; molten iron is literally ‘white hot’. The hottest stars actually radiate most of their energy at the blue end of the spectrum. Under normal circumstances surface temperature fluctuates up and down until there is a balance between the amount of radiant energy received by the surface and the amount energy radiated away.
At Planet Earth’s temperature, most heat is lost as relatively short wavelength infrared radiation, because ‘greenhouse gases‘ block some of the longer wavelengths (Wikipedia’s articles do a good job of explaining the physical laws and processes governing Earth’s energy budget). With no greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the average temperature of Earth’s surface would be about −18 °C, rather than the present average around 15 °C. As explained, for a given mix and concentration of greenhouse gases Earth’s average temperature will rise or fall until the same amount of energy (mainly in the form of infrared) is radiated to outer space as is received from the Sun (mainly in the form of visible light).
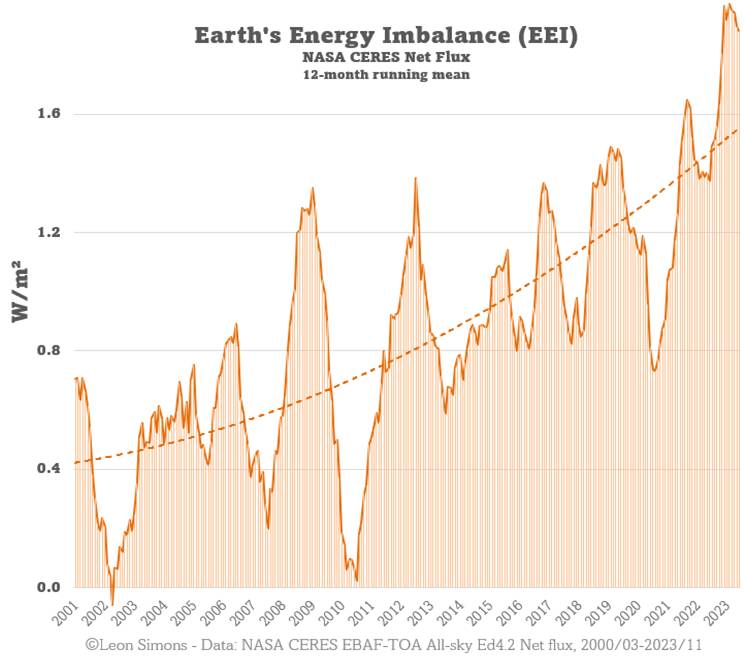
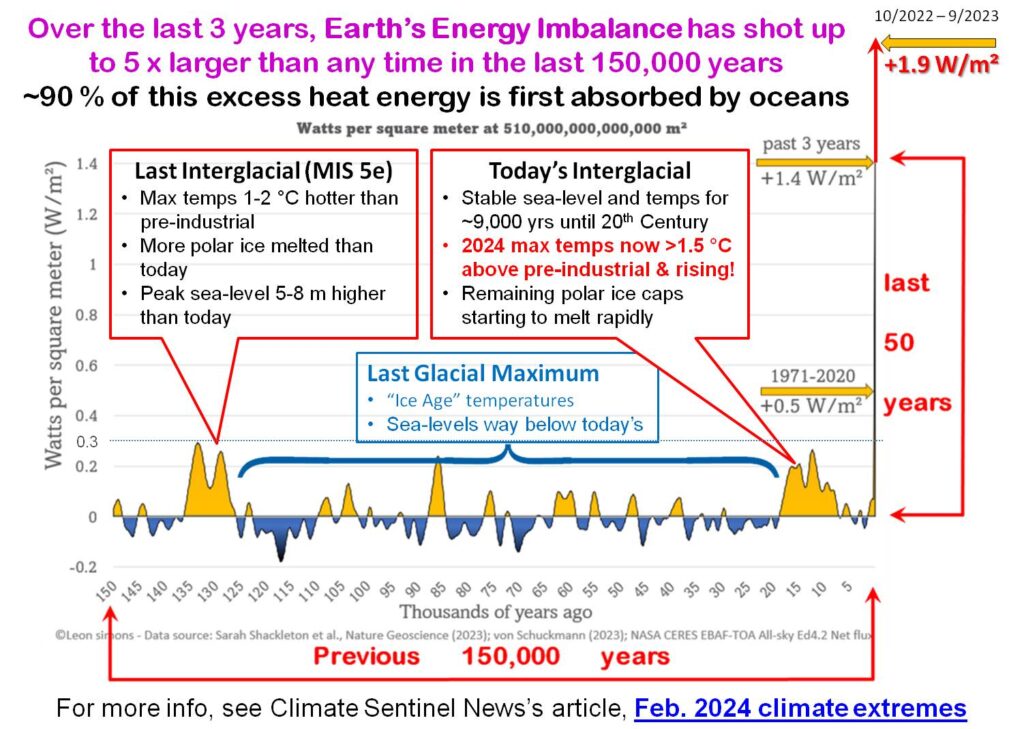
However, Figure 2 shows that is not the case today. Our planet is suffering from what is an extraordinarily rapidly growing energy imbalance that vastly exceeds anything that can be reconstructed from the last 150,000 year geological record of the planet. Currently, 93% of the excess energy is being stored by heating the Ocean. According to Trenberth and Cheng (2022),
About 93% of the extra heat from [Earth’s Energy Imbalance] ends up in the ocean as increasing ocean heat content (OHC). In 2022, the global OHC was the highest on record (Cheng et al 2022) and the global warming signal in OHC is large compared with the natural variability, unlike [Global Mean Surface Temperature], so that trends in OHC can be detected in four years….]
Read the complete article….
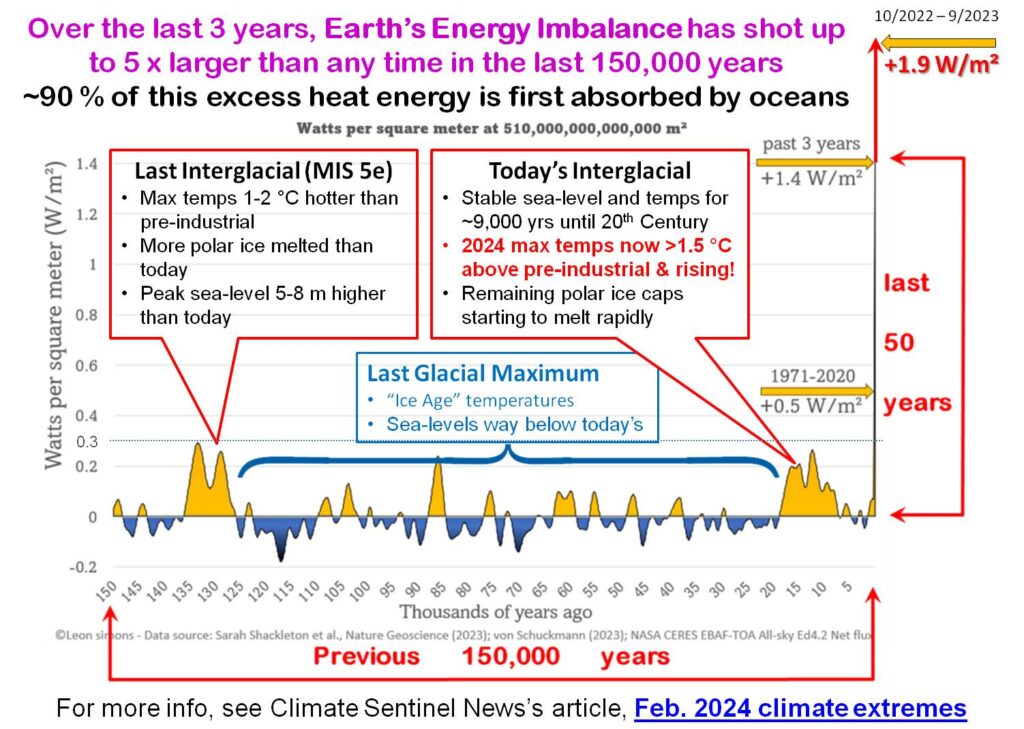
Figure 3 below, shows that this imbalance is rapidly growing in the 21st Century, the latest reading (mid 2023) is around 5 times what it was in 2001. This imbalance is what is driving the rapid growth of sea-surface temperatures shown in Figure 1.
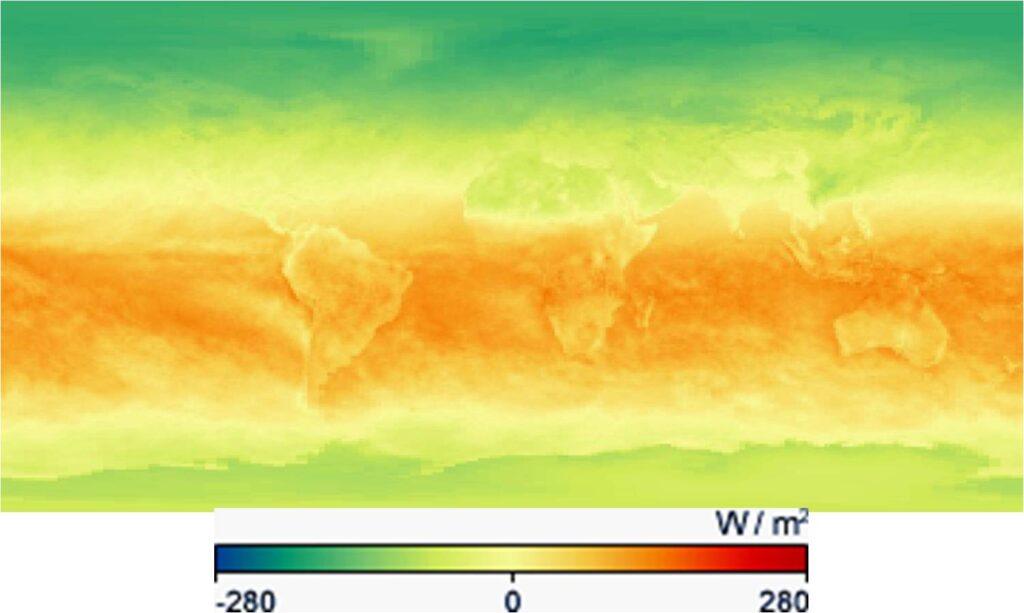
Specifically, net radiation is the sum total of shortwave and longwave electromagnetic energy, at wavelengths ranging from 0.3 to 100 micrometers, that remains in the Earth system. The net radiation is the energy that is available to influence the climate. On a global scale, the net radiation must be zero or else the planet’s overall temperature must rise or fall.
These false-color maps show the net radiation (in Watts per square meter) that was contained in the Earth system for the given time period. Regions of positive net radiation have an energy surplus, and areas of negative net radiation have an energy deficit. The maps illustrate the fundamental imbalance between net radiation surpluses at the equator, where sunlight is direct year-round, and net radiation deficits at high latitudes, where direct sunlight is seasonal. This imbalance is the fundamental force that drives atmospheric and oceanic circulation patterns. (https://neo.gsfc.nasa.gov/view.php?datasetId=CERES_NETFLUX_M)
The only thing that will forestall that flood of excess energy into the oceans making them even hotter is to reverse the imbalance by radically reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere allowing more heat to escape AND by reflecting more of the incident energy back to space before it is absorbed into the oceans.
Regarding reflection, Leon Simmons2 and others have shown that a reflective smog of sulfate aerosols produced by worldwide shipping burning dirty, sulfur-rich diesel fuel slowed ocean warming by a significant amount. This source of sulfur emissions largely stopped when the International Maritime Organization shipping regulations increasingly restricted sulfate emissions (see Hansen, Sato, Simons et al., 2023. Global warming in the pipeline. Oxford Open Climate Change). This unplanned experiment and the Mt Pinatubo eruption in 1991 demonstrated that sulfate aerosols could measurably reduce the amount of solar heat absorbed by Earth. However, given that the aerosol particles basically consist of concentrated sulfuric acid that eventually falls into the living biosphere to acidify land and ocean, sulfate aerosol production will probably cause more problems than the additional heating allowed by clean air. IPCC climate modeling grossly under represents the energy imbalance (Schmidt et al., 2023. CERESMIP: a climate modeling protocol to investigate recent trends in the Earth’s Energy Imbalance. Frontiers in climate; see also Leon Simons X-Twitter thread).
Ocean currents distribute excess heat from hottest areas to the rest of the planet. Far more heat energy enters the air via convection and increased humidity carrying latent heat in vaporized water from the oceans than is absorbed directly from Solar radiation. Heated land also contributes energy to the atmosphere via evaporation and convection.
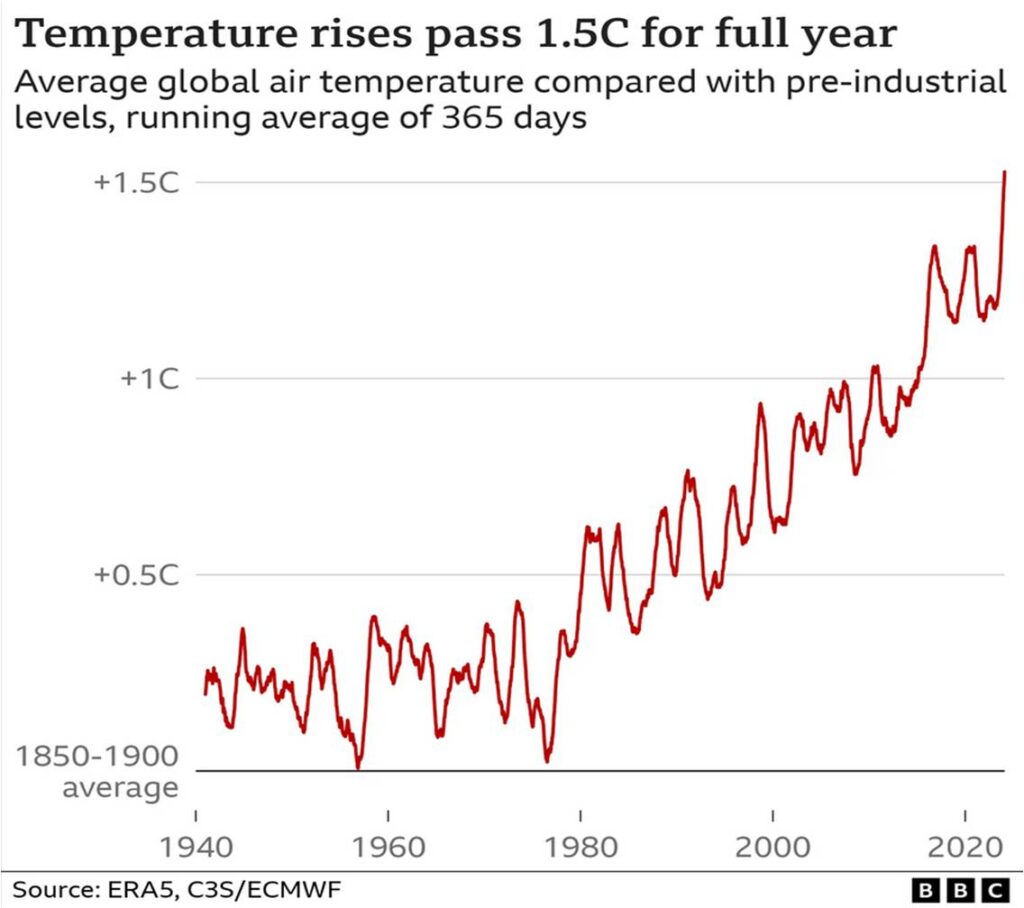
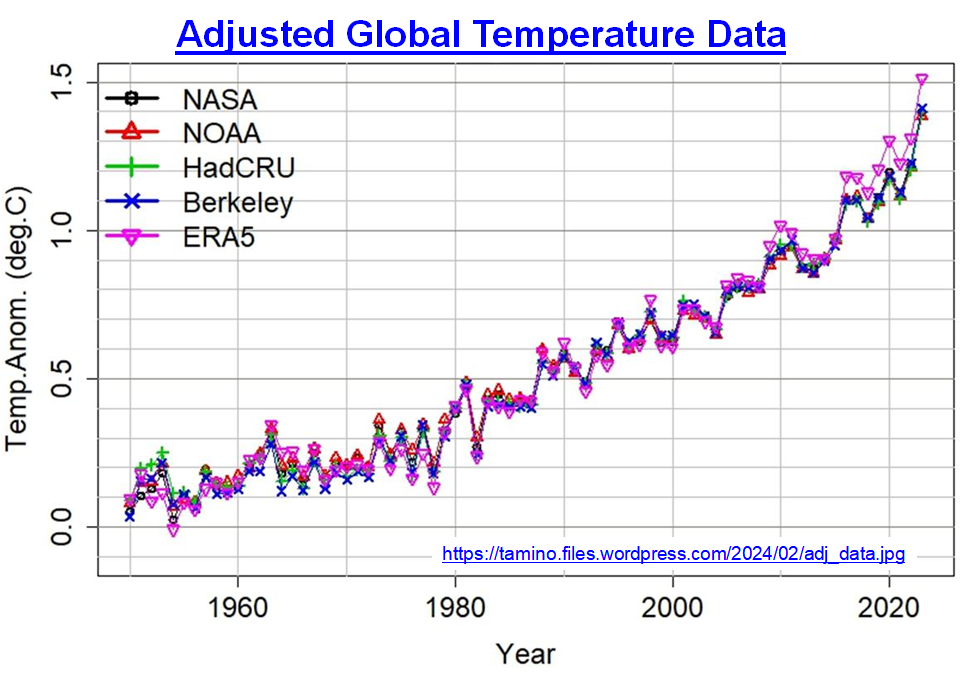
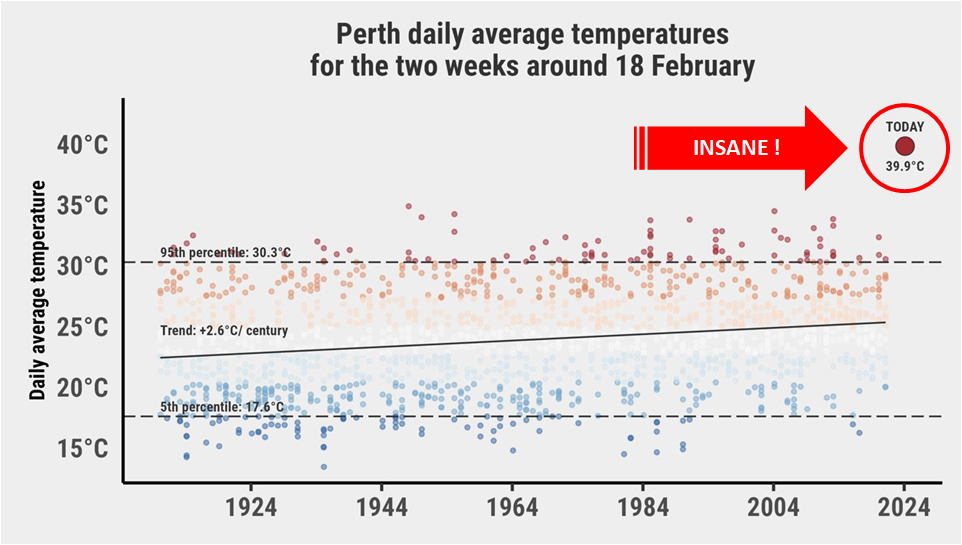
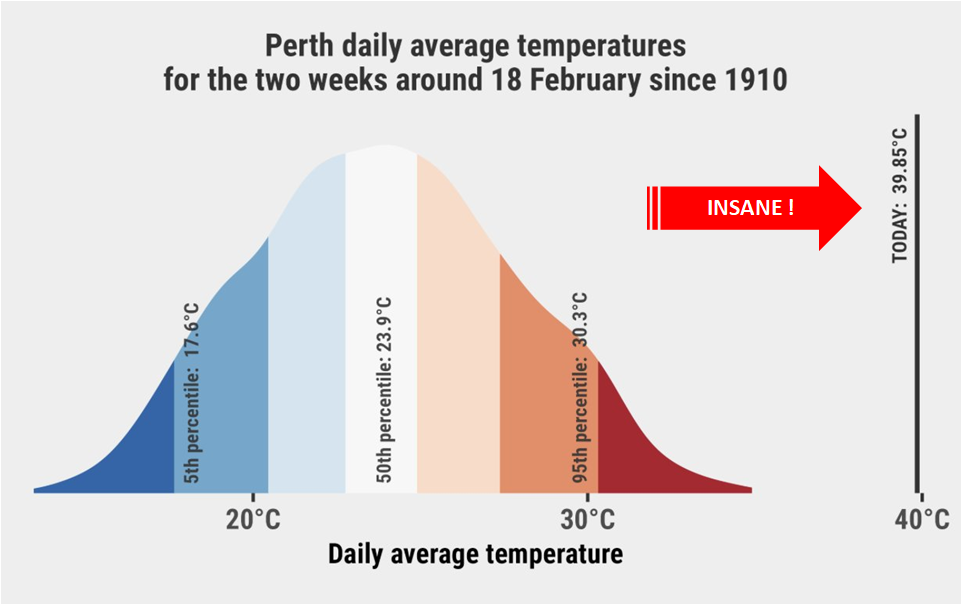
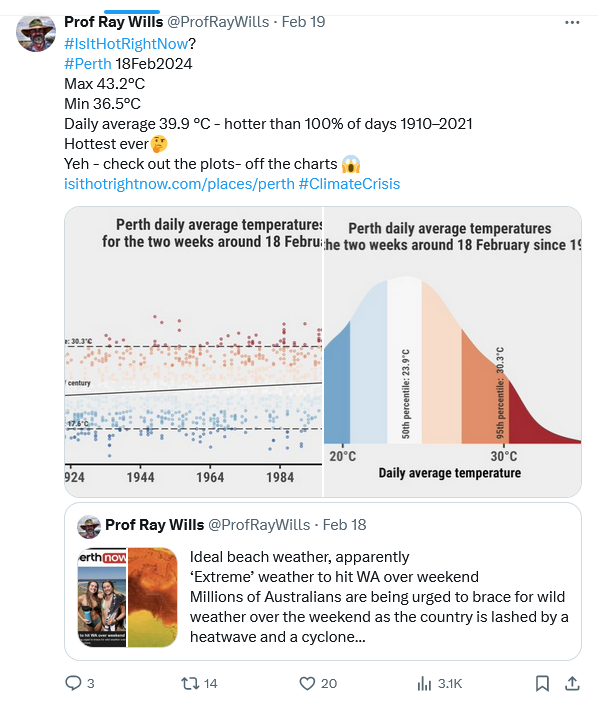
Figure 6a. On 18 February, the air temperature in Perth, Western Australia was so far beyond the kinds of record highs that can be expected from random variation around some “normal’ value for the time of the year that it was unimaginable — until it was recorded.
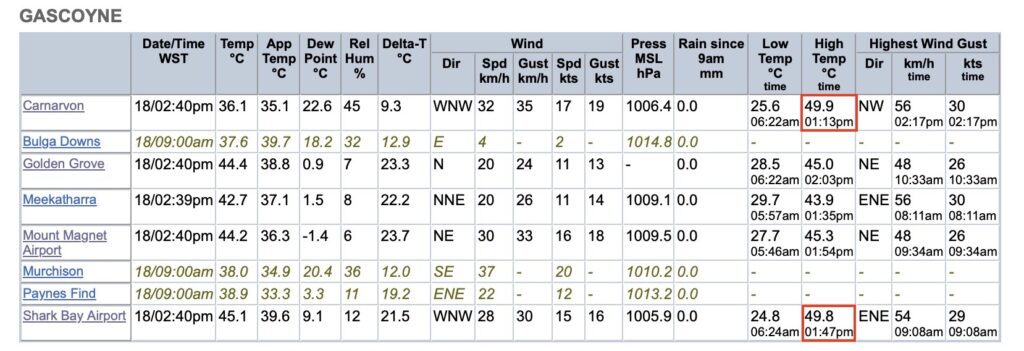
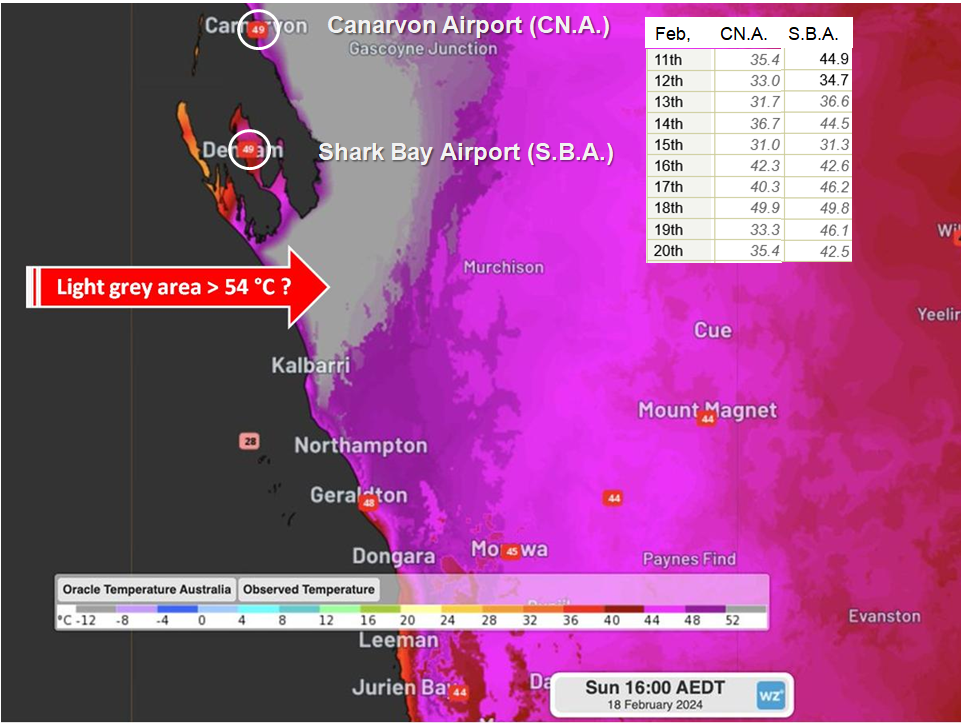
And then it was much hotter further up the Western Australian coast from Perth! See Sophie McNeil – https://twitter.com/Sophiemcneill/status/1759174092597715078: 10 °C hotter in Canarvon and Shark Bay Airport; and based on satellite measurements, probably at least 14 °C hotter on the flatland inland of Shark Bay where there are no ground-based weather stations to record the measure. Closer to the boiling point of water than the freezing point! and well above temperatures where unprotected humans could survive. WeatherZone Business highlights these observations on their Instagram account.
This heating of the oceans (Figure 1) and atmosphere (Figures 4 and 5) caused by the energy imbalance is already causing a range of catastrophic extreme weather events around the world. However, before exploring these further we should first consider what causes the energy imbalance.
Global warming is caused by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases emitted by and as a consequence of human activities.
Until the accelerating trends illustrated in the following graphs can be reversed to the point that the “increase” graphs extend into negative territory and the “concentration” curves begin to curve downward to show decreasing concentrations, physical laws determine that forcing of the energy imbalance (Figure 3) will continue to grow ever more lethal for the biosphere. The main forcing factor is the still accelerating rising concentration of infra-red blocking greenhouse gases.
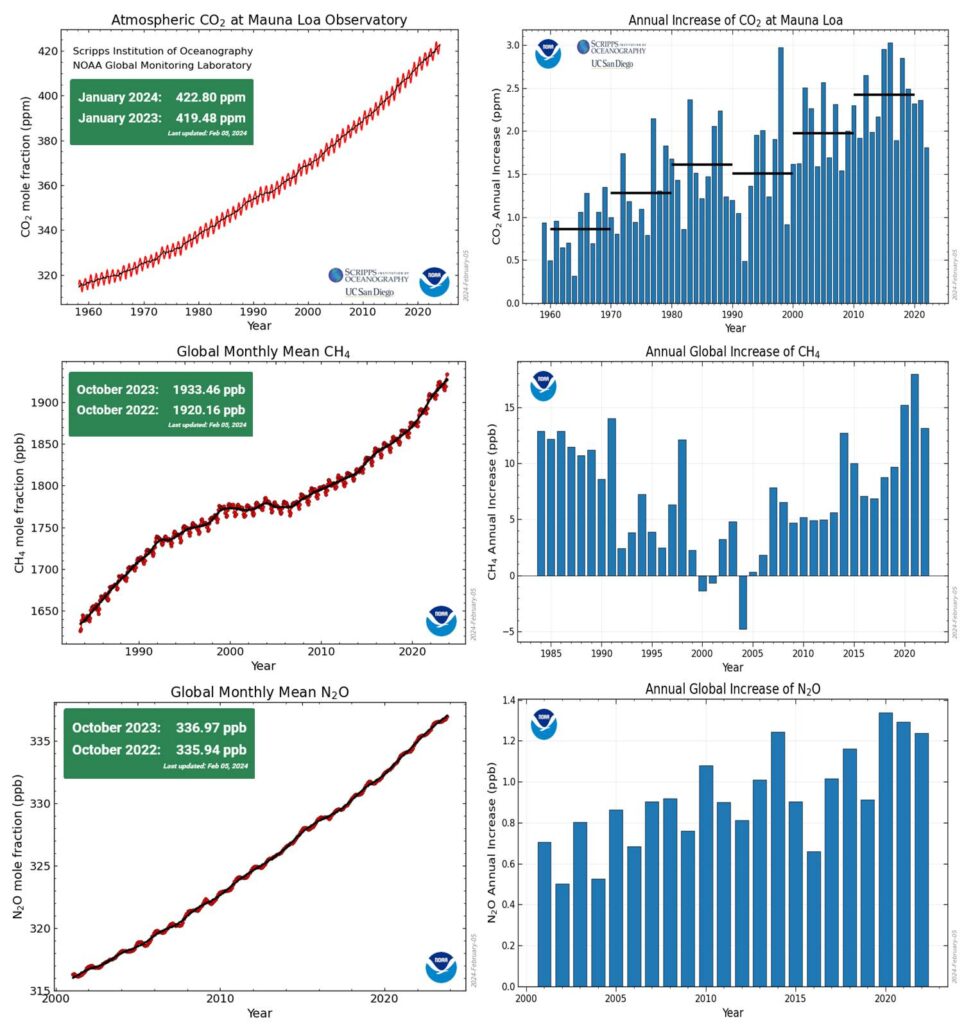
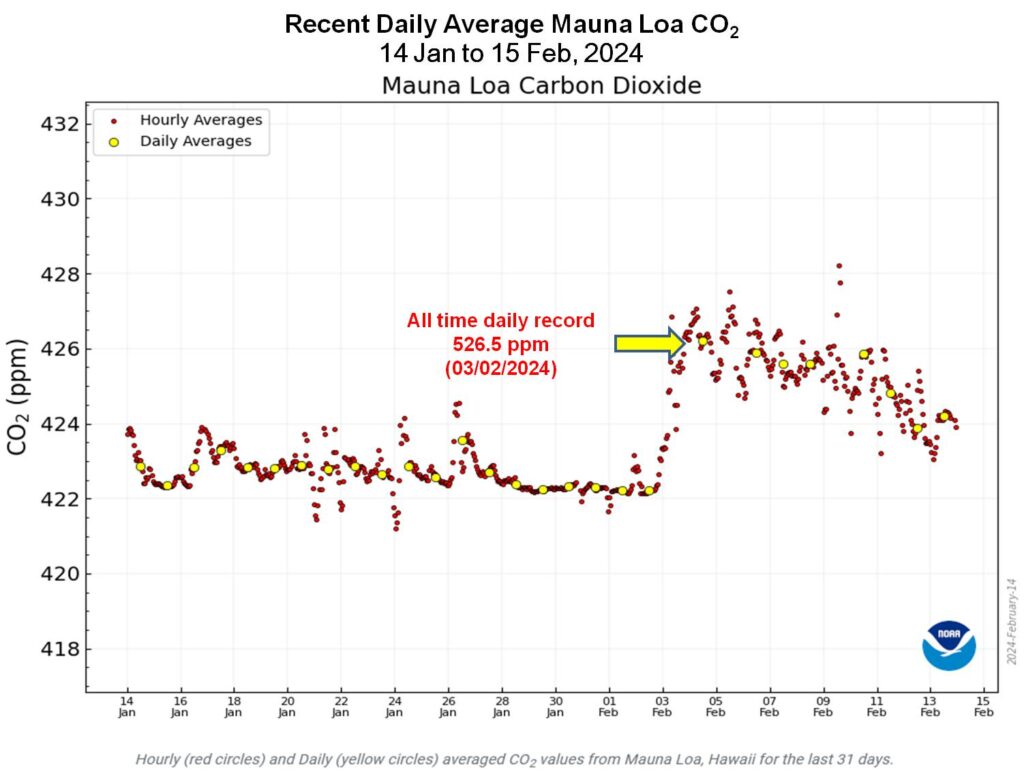
The record for direct CO2 measurements, a carbon dioxide concentration of 426.5 parts per million (ppm), was observed on Friday Feb. 3 2024 when the wind over Mauna Loa shifted to more northerly. This brought air in from North American and East Asian industrial areas thousands of miles upwind.
These measurements are made in many locations around the world as indicated on the following world map.
Wherever in the world these trends are measured, the increasing concentrations of principal greenhouse gases show similar patterns. For example:
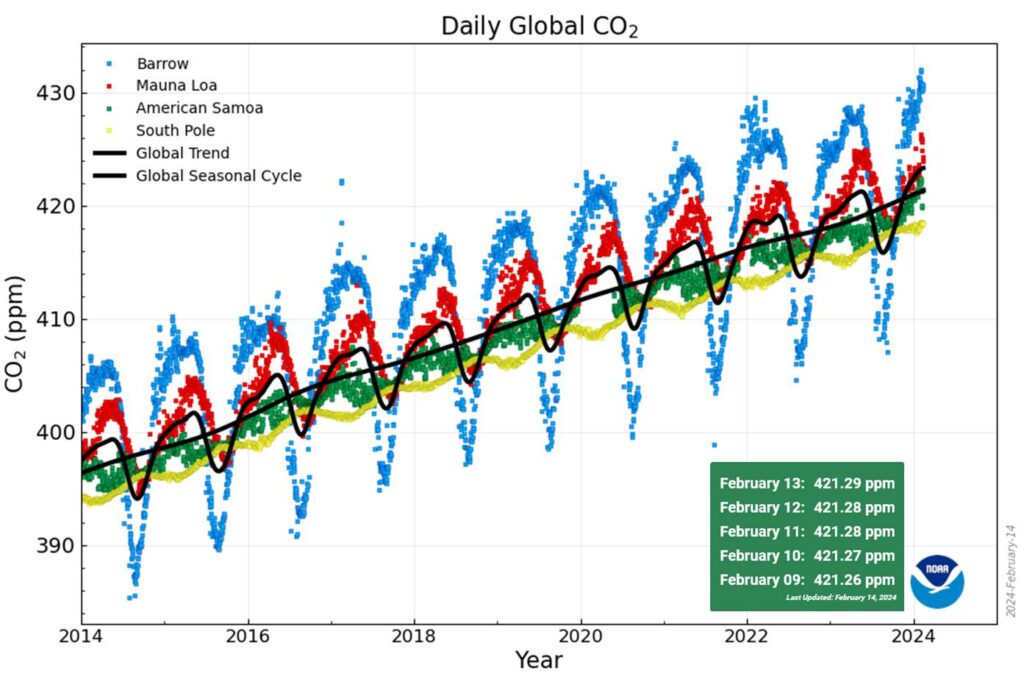
The figure shows daily averaged CO2 from four GML Atmospheric Baseline observatories; Barrow, Alaska (in blue), Mauna Loa, Hawaii (in red), American Samoa (in green), and South Pole, Antarctica (in yellow). The thick black lines represent the average of the smoothed seasonal curves and the smoothed, de-seasonalized curves for each of the records. These lines are a very good estimate of the global average levels of CO2. Details about how the smoothed seasonal cycle and trend are calculated from the daily data are available here.
The four locations in Figure 10 show relative decreases going from north to south. A majority of emissions are made in the Northern Hemisphere and a majority of the net draw-down into the biosphere occurs in the oceans of the Southern Hemisphere.
Mauna Loa and South Pole data from Scripps CO2 Program.
The way in which this excess heat is distributed around our planet has profound implications for the planetary biosphere and human survival in it as expressed in the inevitable weather and climate extremes as the world warms beyond our physiological limits of adaptation.
Ocean circulation is the major engine distributing excess heat around the planet.
We know a great deal about the dynamics of ocean heating and the distribution of heat through the international Argo Float program (see Fig. 12 for a link describing the Argo program). In addition to the direct physical measurements by Argo Floats, sea surface temperatures are also based on scans of the whole of the Earth’s surface by numerous satellites launched by several different countries.3

Wikipedia’s Ocean Heat Content article explains how the ocean redistributes its heat content around the planet.
Heat absorbed in the ocean is circulated around the planet by ocean currents, where much of it is transferred over time to the atmosphere by direct contact.
AMOC under threat
Earth’s ocean currents are critical in distributing and regulating heat over the entire planet. These currents are largely driven by temperature differences between polar and tropical waters. Although the Atlantic Ocean is smaller than the Pacific, the Atlantic circulation is probably the most important because it is the primary connection between the Arctic Ocean and the tropical regions. (The shallow Bering Strait between NE Asia and Alaska completely blocks the exchange of deep waters between the Pacific and the Arctic Ocean). Wikipedia explains in detail:
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) is a system of surface-level and deep currents in the Atlantic Ocean which are driven both by changes in the atmospheric weather and thermohaline changes in temperature and salinity. These currents collectively make up one half of the global thermohaline circulation that encompasses the flow of major ocean currents. The other half is the Southern Ocean overturning circulation, and both play highly important roles in the climate system.…
Also, the most extreme oceanic heating has taken place in the North Atlantic (where shipping traffic has been the most concentrated and where there has been the greatest reduction in sulfate emissions).
Hot water in the North Atlantic does two things:
- It warms the surface waters in the Arctic.
- Excess heat in the ocean and in the air heated by the ocean speeds the melting of glaciers to dilute the salinity of the ocean at their feet (and raise sea levels).
Both factors work together to reduce the density of the northern waters to the point that they are no longer able to sink below relatively dense mid-level waters to form the Atlantic Deep Water flowing back to the tropics, leaving the warm currents (e.g., the Gulf Stream) bringing heat up from the south no place to go, stopping the flow. Paradoxically, this blockage would probably allow NE North America and NW Europe to become extremely cold over winter.
Leon Simons’s thread below explains:
Marine dieoffs and the collapse of marine ecosystems
As the oceans rapidly grow hotter, we’ll soon see the extinction of keystone coral species and collapses of ecosystems they support. Not only will we lose many species but their rotting remains will emit greenhouse gases such as CO2 and poisonous hydrogen sulfide gas…. The additional CO2 emissions will add to positive feedback increasing the energy imbalance –> global heating –> sea surface temperature.
In Australia and elsewhere, other than coral bleaching and death (e.g., the Guardian’s latest – Bleaching fears along 1,000km stretch of the Great Barrier Reef), we are also seeing dieoffs of mangrove, sea grass, and kelp. For several years we have known these were happening, but as the ocean continues to warm, the die-offs will take place faster and more comprehensively until the species (and the ecosystems they support) are lost entirely (i.e., become extinct).
Ice melting and sea-level rises
Warm oceans carry prodigious amounts of heat into polar zones, to substantially increase the rate of ice melting and raising polar temperatures to slow and eventually stop re-freezing. There is ample evidence for a greatly increased rate of melting.
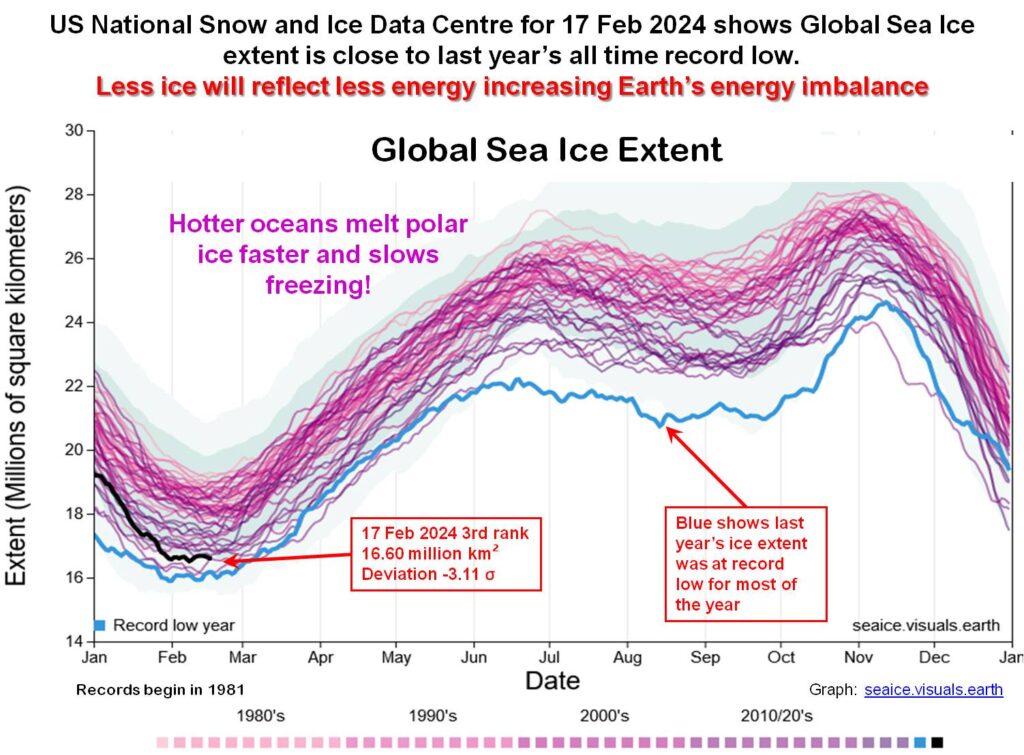
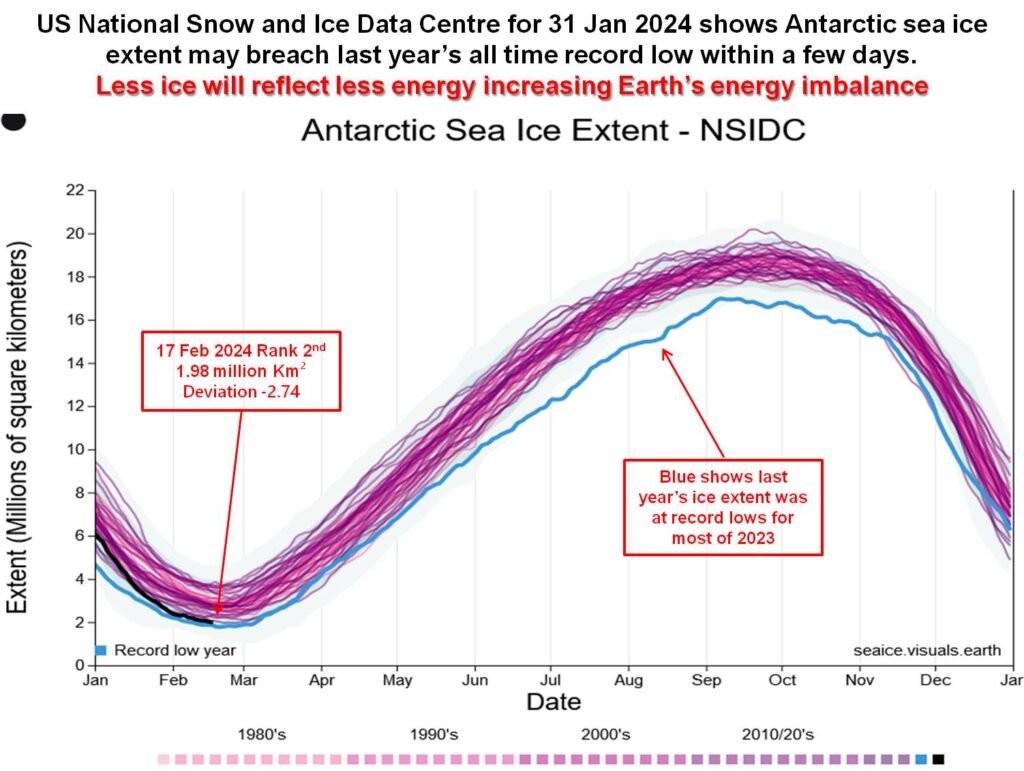
Antarctic sea ice extent is currently very close to its all-time low recorded last year. As of March 1, this year’s extent passed its low point as second lowest ever and has now risen to 4th lowest . In any case, at an extent of only 2 million km2 the Antarctic Ocean will not be reflecting much heat away from the planet.
Warming produces melt-water that lubricates the sliding of ice into a hot ocean
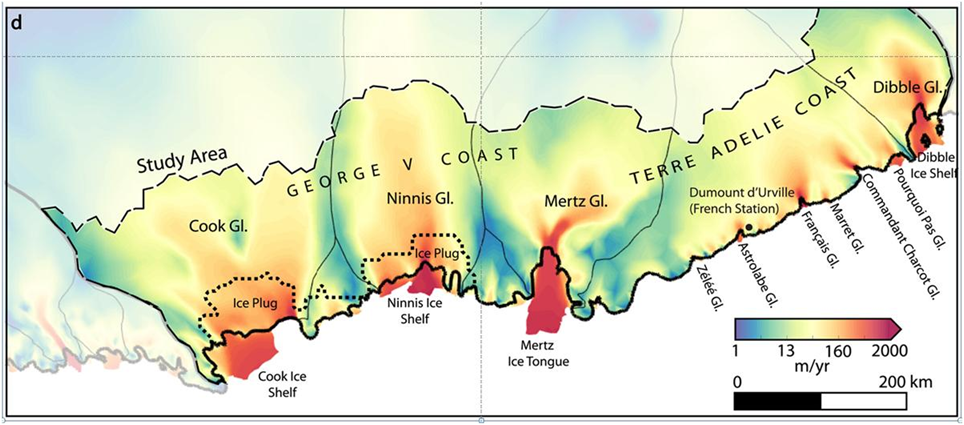
East Antarctica’s Adélie-George V Land has been relatively stable over the last few decades. However, this region contains the Wilkes Subglacial Basin, which has a downward-sloping bed inland of the grounding zone. This could make irreversible retreat possible if warming seawater off the coast enters beneath the ice sheet…. We find that areas near the outflow of the Wilkes Subglacial Basin, critical in maintaining the stability of the region, might consist of mixed frozen-bed and thawed-bed or near-thawed conditions on the scale of tens of kilometers across. This finding is important since the extent of basal thaw affects how easily ice can flow or slide over the bed. If parts of the bed are close to thawed, this could make Adélie-George V Land more sensitive to climate forcing, possibly resulting in mass loss. For media articles see also: https://news.stanford.edu/2024/02/05/stable-parts-east-antarctica-ice-may-close-melting/; California-size Antarctic ice sheet once thought stable may actually be at tipping point for collapse.
Where Antarctica is concerned, its land ice has the potential to cause major rises in global sea levels compared to what Greenland can do. In 2024, East and West Antarctica’s riskiest glaciers are still plugged by grounded ice. However, as the article referenced above (Figure 18) discusses, several of the plugs on the largest glaciers are showing signs of impending collapse.
Sea levels are rising at an accelerating rate as a consequence of melting land ice (mainly Greenland and Antarctica)
In addition to the rise in sea level due to the addition of meltwater from land ice, ocean water expands in volume as its increasing heat content increases its temperature.
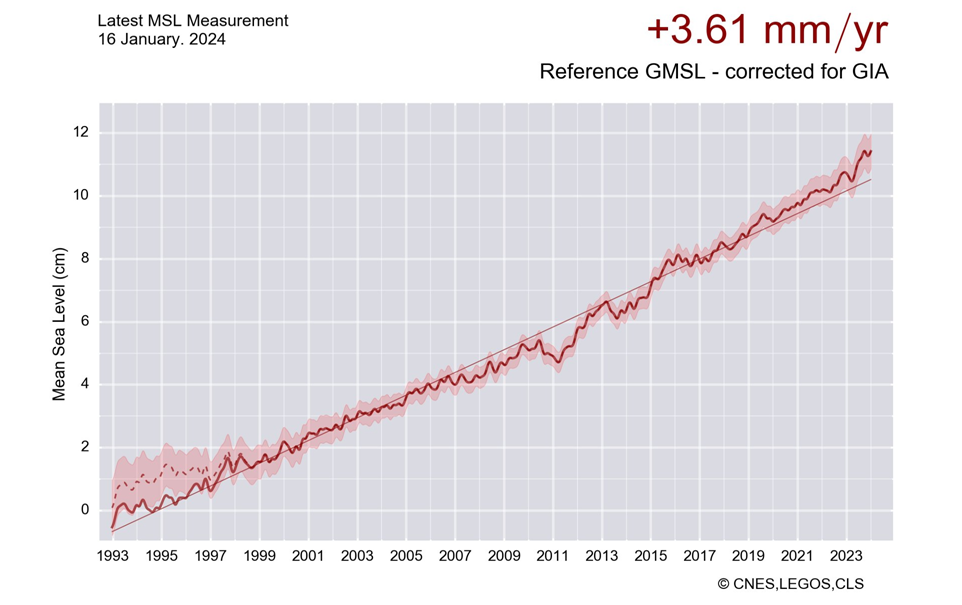
As global warming occurs, a direct reaction of the climate system is the sea level rise. This rise results from seawater expansion as a response to the temperature increase and addition of water from land-ice sheets and glaciers melting. Precise monitoring of the sea level rise is made possible using altimetry satellites that help understanding climate change and its socioeconomic consequences. The Global Mean Sea Level (GMSL) has thus become a key indicator of climate change.
The reference global mean sea level (GMSL) based on data from the TopEx/Poseidon, Jason-1, Jason-2, Jason-3 and Sentinel-6MF missions from January 1993 to present, after removing the annual and semi-annual signals and applying a 6-month filter. By applying the postglacial rebound correction (-0.3 mm/yr), the rise in mean sea level has thus been estimated to 3.6 mm/year with an uncertainty of 0.3 mm/yr.
Note that over the last quarter of year 2022, Sentinel-6 MF is affected by an inaccurate radiometer calibration error resulting in an overestimation of the wet tropospheric correction and therefore of the GMSL by about 5 mm (see issue #9170 of EUMETSAT User Notification Service at https://uns.eumetsat.int/ ).
Analyzing the uncertainty of the altimetry observing system yields to construct an uncertainty envelop for the GMSL climate data record (shaded area in the figure above).
The dashed line displayed over 1993-1998 is an estimation of the GMSL evolution after correction of the TOPEX-A instrumental drift (Cazenave WCRP 2018). It is estimated from empirical correction derived by comparing altimetry and tide-gauge sea level data (see more details in Validation). The TOPEX-A instrumental drift led to overestimate the GMSL slope during the first 6 years of the altimetry record. Accounting for this correction changes the shape of the GMSL curve, that is no more linear but quadratic, indicating that the mean sea level is accelerating during the altimetry era (1993-to present, Beckley et al. 2017, Nerem et al. 2018). Currently, this empirical correction is not applied to the AVISO GMSL dataset, wainting for the ongoing TOPEX reprocessing by CNES and NASA/JPL.
The most immediate dangers from ice melting are in the Arctic Ocean
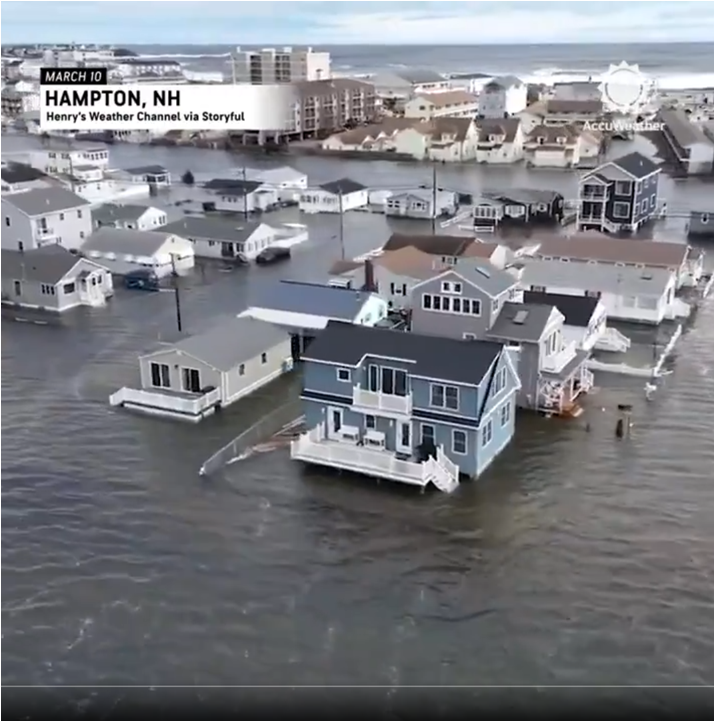

@accuweather. Drone video shows the extensive flooding in Hampton, New Hampshire, on Sunday morning, just two months after the same area was hit with significant flooding. https://twitter.com/accuweather/status/1766932084961235072. Melting land ice adds more water to the ocean. As water grows warmer it expands — increasing in volume. See video of beach erosion in nearby Massachusetts.
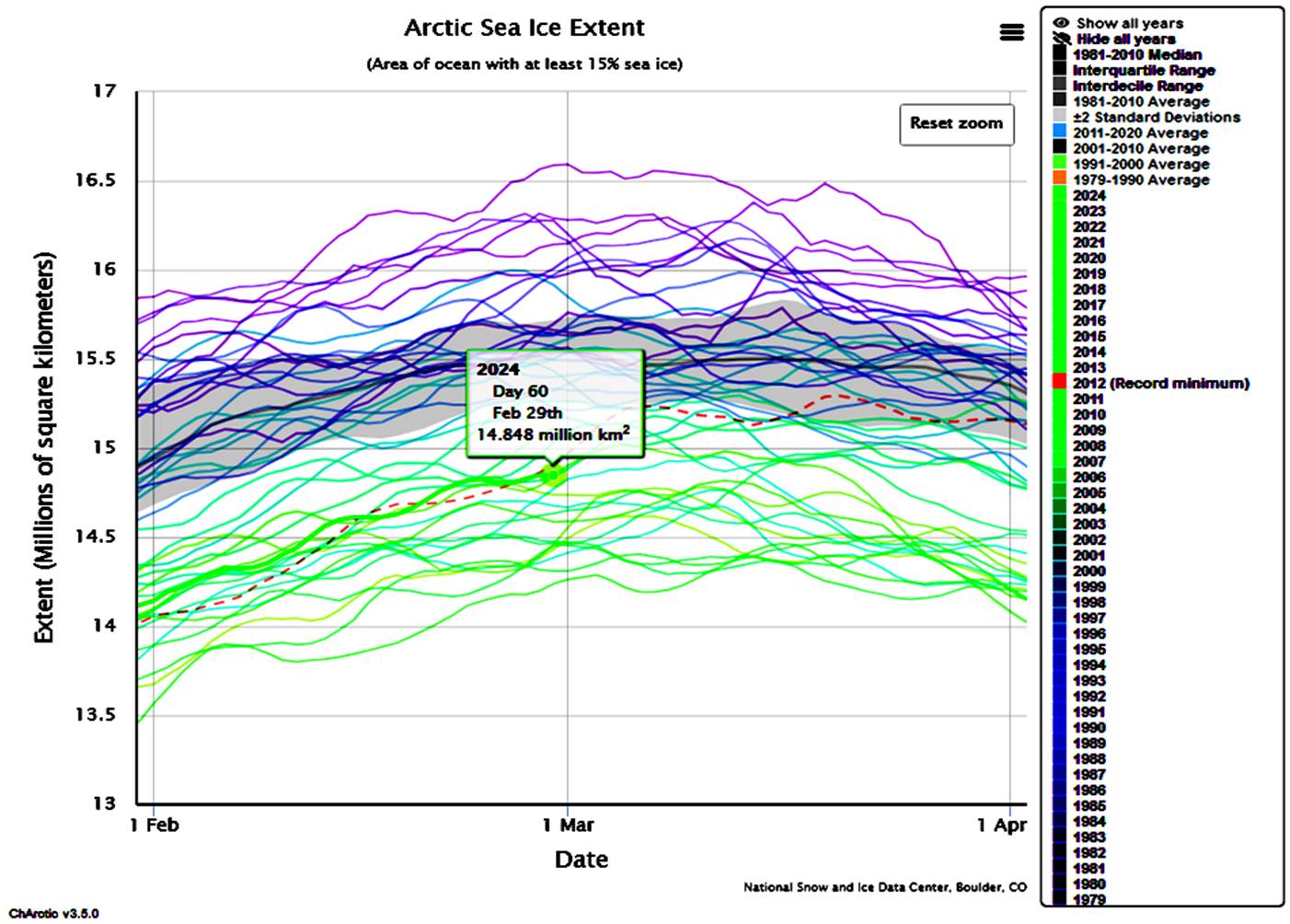
The reflection of a significant percentage of solar energy over many days of 24 hour summer sunlight Arctic Ocean’s sea ice and Greenland’s ice cap is an important component in Earths energy balance. Similarly, Greenland’s potential contribution to total sea level rise is limited by its small size compared to Antarctica. However, over the near term, Greenland’s proximity to the rapidly warming North Atlantic Ocean and an Arctic Ocean likely to be ice-free and also rapidly warming in the next few years puts the entire Greenland ice cap at risk for rapid melting. What happens in the Arctic over the next few years will profoundly affect the entire world.
Changes in the in the reflectivity (“albedo”) of the Arctic can have a profound effect on Earth’s planetary weather system. Sam Carana’s article started in 2012, Albedo, latent heat, insolation and more, explains the roles and feedbacks between ice melting, insolation, and temperature and explores the potential consequences of these changes.
The following images provide the evidence to bring the story up to February this year. They drive home the message that we are probably on the cusp of a critical tipping point to a new climate regime governed by an ice-free and rapidly warming Arctic Ocean that governs climate for most of Planet Earth.
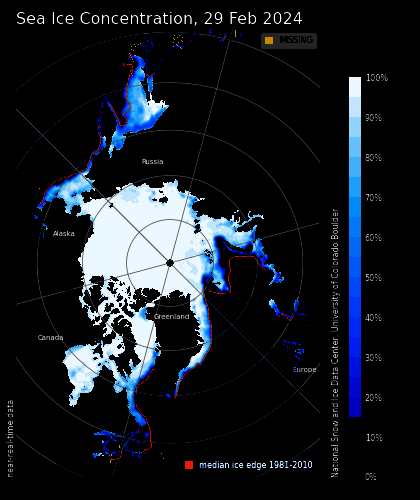
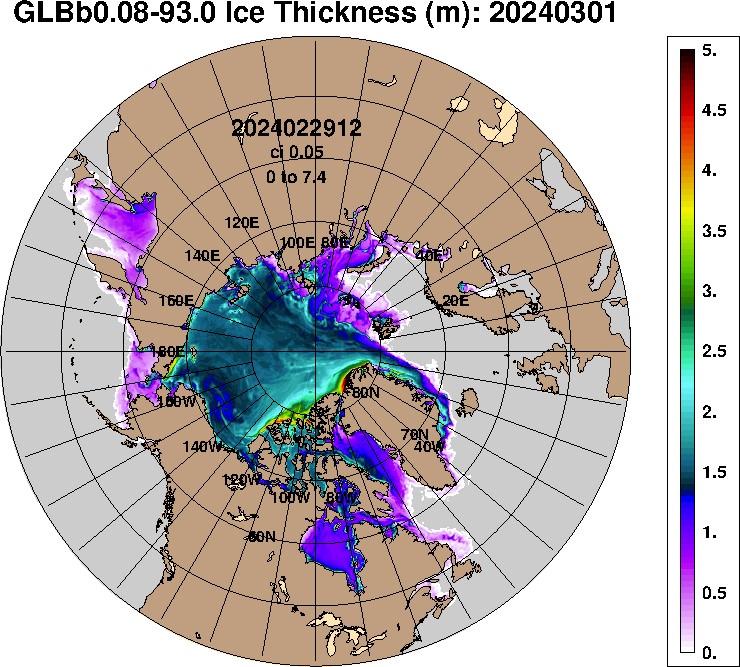
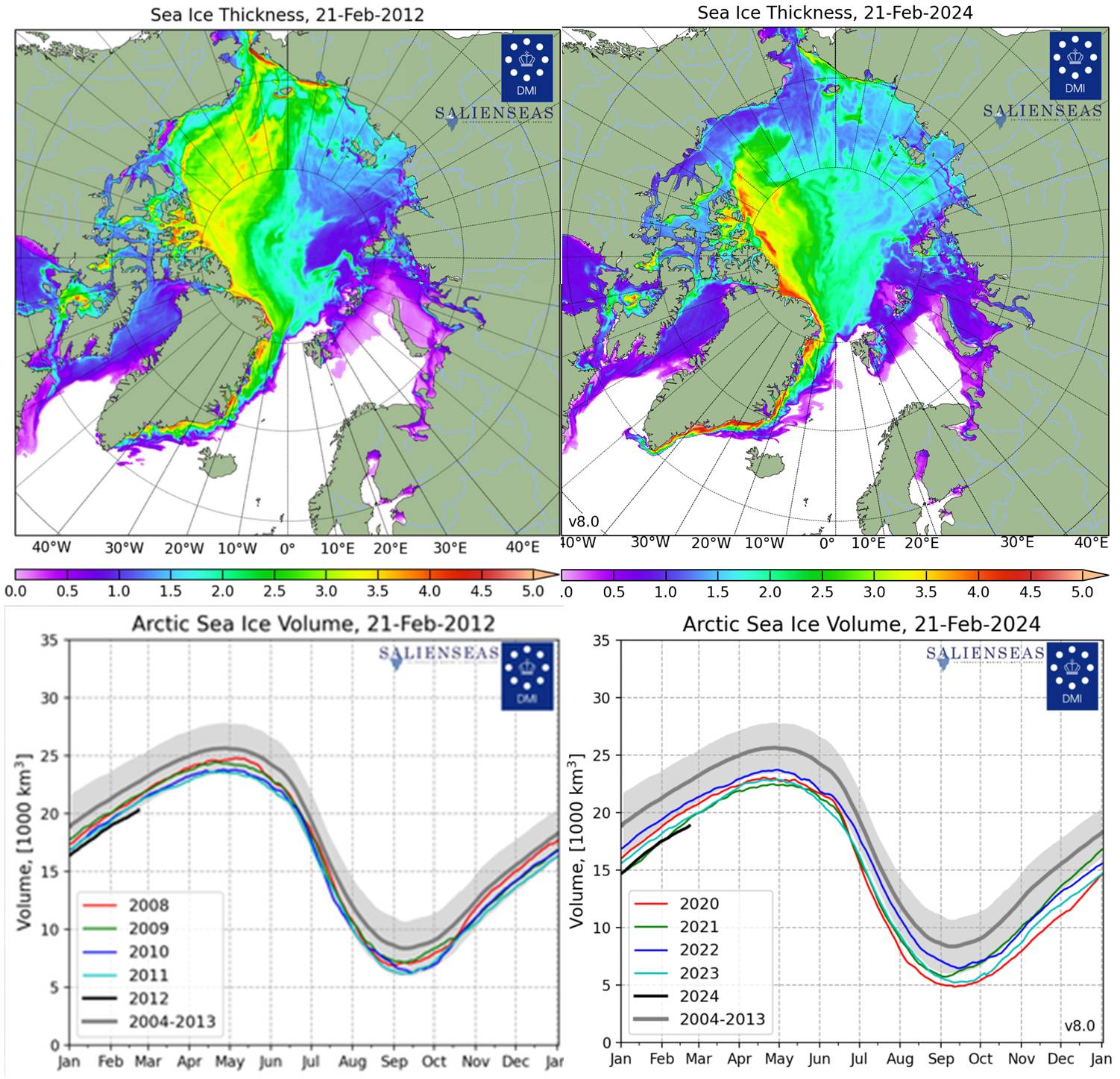
Real-time 1/12° Global HYCOM+CICE Nowcast/Forecast System. Close to the winter maximum extent, except for a tiny sliver of thicker ice piled up close on the northernmost areas of the Canadian Archipelago and Greenland. The thickest sea ice anywhere on the Arctic ocean is < 2.6 m. Over half the coverage is < 1.5 m. In the early 1980’s large areas of the Ocean north of Canada and Alaska were covered by 4 to even 5 m thick ice.
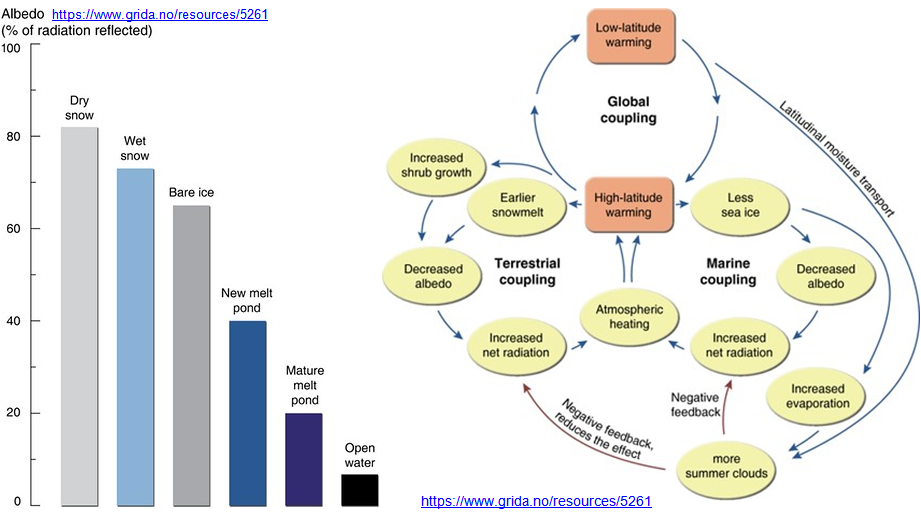
The albedo for different surface conditions on the sea ice range widely, from roughly 85 per cent of radiation reflected for snow-covered ice to 7 per cent for open water. These two surfaces cover the range from the largest to the smallest albedo on earth. Melting snow, bare ice and ponded ice lie within this range. There is a general decrease in the albedo of the ice cover during the melt season as the snow-covered ice is replaced by a mix of melting snow, bare ice, and ponded ice. As the melt season progresses, the bare ice albedo remains fairly stable, but the pond albedo decreases. During summer the ice cover retreats, exposing more of the ocean, and the albedo of the remaining ice decreases as the snow cover melts and melt ponds form and evolve. These processes combine to form the ice–albedo feedback mechanism.
Year: 2016.From collection: Global Outlook for Ice and Snow: Albedo of sea-ice surface types – https://www.grida.no/resources/5219; Feedbacks associated with albedo changes – https://www.grida.no/resources/5261. Cartographer: Hugo Ahlenius, UNEP/GRID-Arendal.
Arctic temperatures are already rising at a rate 2-4 times faster than for the Earth as a whole (referred to as Arctic amplification. This reduces the difference between subtropical-temperate zones and polar regions that drives jet streams. With less energy to work with the jet streams slow and begin to wander chaotically that in turn enables the development of lethally extreme heatwaves or cold outbreaks in sub-polar and temperate zones that can remain stationary for days or even a week or more.
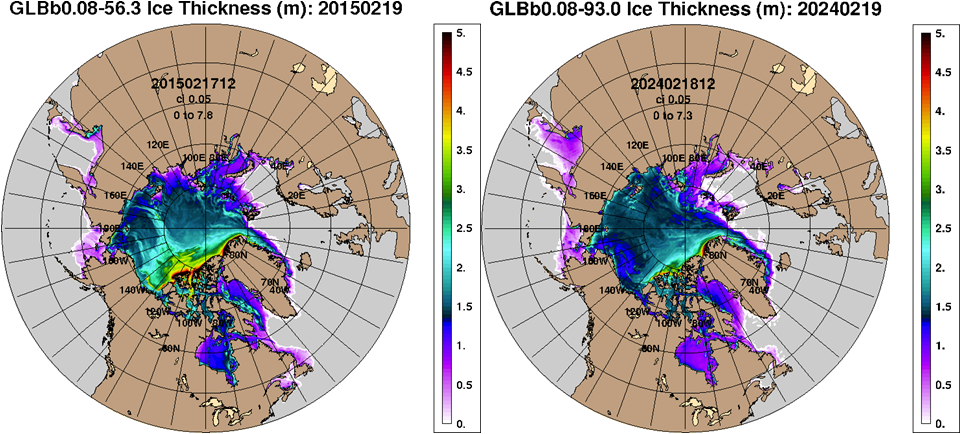
With some fluctuations, for the last several decades the extent of Arctic sea ice has been declining to annual minimums in the 2020s to around half the area the ice covered in the early 1980s. With much less apparent impact up to now, the thickness of winter ice has also been diminishing significantly, to the point that within a very few years the extent of midsummer ice will show a catastrophic drop to virtually nothing as its thickness drops to zero, as several national technologies have shown in the following thickness maps.
Given geopolitical conditions around the margins of the Arctic Ocean, the US Navy is particularly concerned with ice conditions in relationship submarine and surface ship navigation. The CICE Nowcast system developed by the US Navy Research Labs, was only operational beginning in 2015, but even beginning from then, a year before the minimum ice extent yet was recorded in 2016, today’s ice thickness is conspicuously less than ~ a decade ago.
The next series of graphics are from European sources – mainly from the Danish Meteorological Institute’s Polar Portal. Greenland and the Faeroe Islands are autonomous territories of Denmark, so their waters are territorial waters of Denmark – which accounts for Denmark’s longtime concern with navigability and sea ice conditions in the Arctic and North Atlantic.
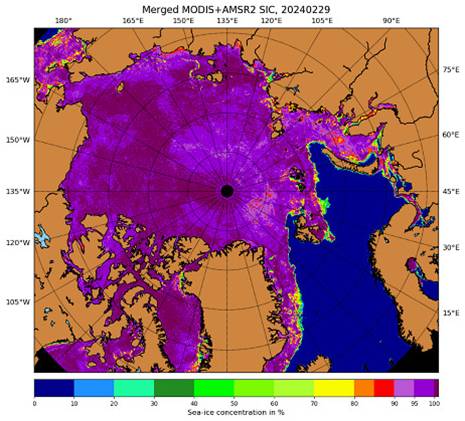
Some of the clearest and most intelligible data outputs of sea-ice changes are produced by University of Bremen’s research group on “Remote Sensing of Polar Regions“. Several of their programs connect directly with the EU’s Copernicus programs in climate science. Compare the observations below with US and Danish systems and are explicitly validated against direct physical measurements from buoys and ice-breaking ships and sensors placed directly on the ice floes.
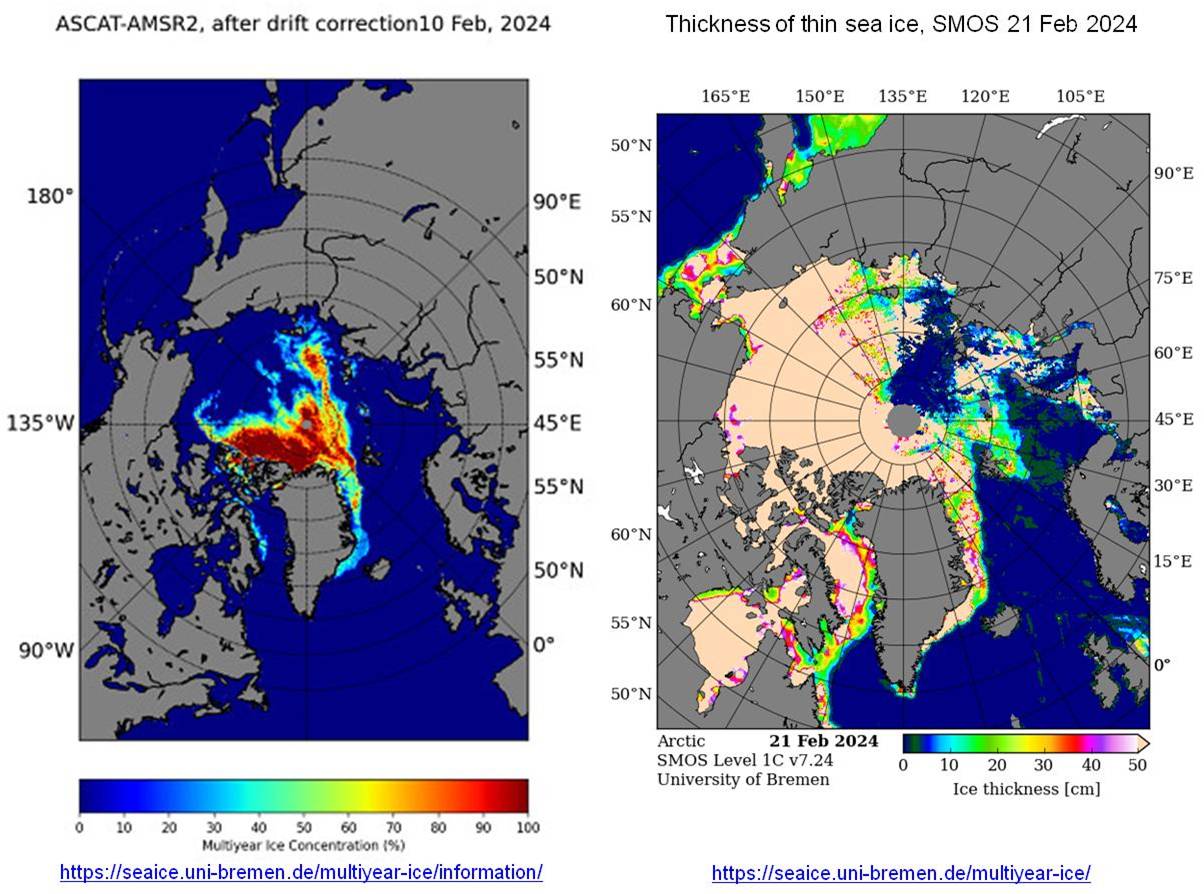
The conclusion to be drawn from the body of remote sensing observations (backed up by on the ice measurements from oceanographic cruises such as the icebreaker Polarstern‘s voyages in the MOSAiC program) is that much of the ice sheet covering most the Arctic Ocean over summer, is presently so thin and broken in winter that it is teetering on the brink of dispersal and complete melting over summer, possibly as early as this year or the next. Replacing the reflective ice with close to totally absorptive blue ocean as shown in areas currently lacking multi-year ice (Figure 24, left) will substantially increase Earth’s energy imbalance. Surrounded by warm water and rising temperatures, any remaining multi-year ice will also soon melt. Depending on how fast summer’s 24 hour solar heating warms the surface waters well above the freezing point, the Arctic Ocean may soon remain ice-free over winter as well…..
For further background, see Polyakov et al. (2017). Greater role for Atlantic inflows on sea-ice loss in the Eurasian Basin of the Arctic Ocean. Science.
One more set of ice observations seems relevant to support the perilous state of Earth’s cryosphere.
Polar ice and its feedback into polar and global air temperatures
The Danes’ long-term concerns about Arctic ice and weather has provided another set of charts that is particularly informative about the interactions between air temperature and sea ice that is likely to impact on future climate conditions (Figures 30 and 31).
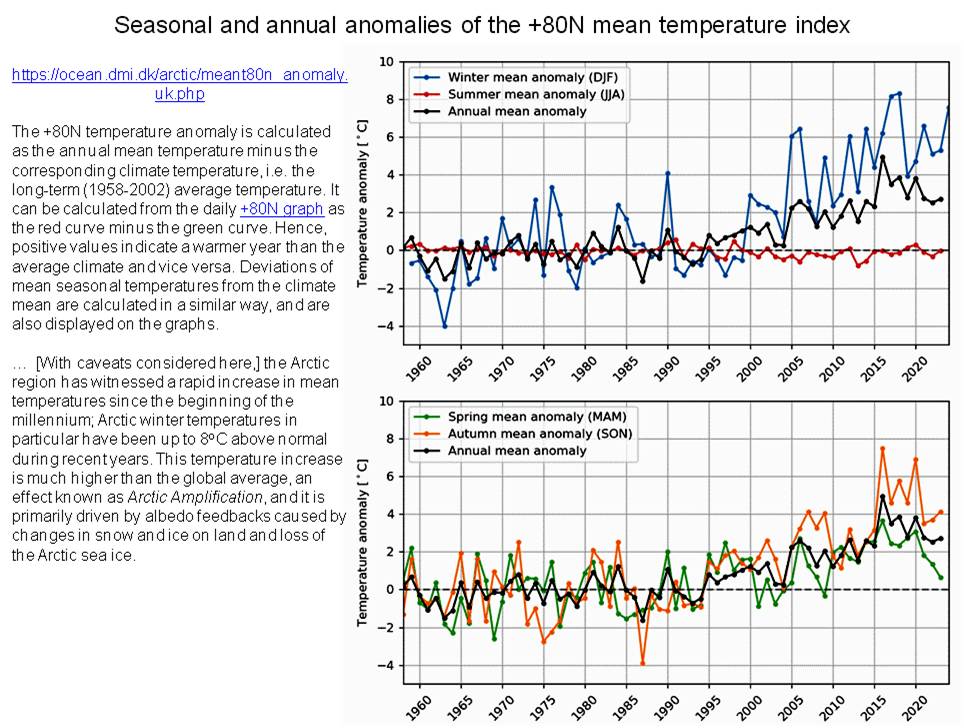
Figures 30 and 31 illustrate an important phenomenon that will reveal itself as a step change in temperatures over the Arctic Ocean – possibly as soon as this year’s northern summer. Spring, autumn, and annual temperature anomalies began rising above the 1958-2002 baseline temperature around 1995. By 2015 they were between 2 and 4 °C above the baseline. The winter anomaly was between 4 and 8° higher than the baseline: offering clear examples of arctic amplification.
Seemingly paradoxically, the summer anomalies have continued to track the baseline anomaly quite closely through the entire measurement period. Actually, this just represents the physical fact that melting a given amount of ice absorbs as much energy as it would take to heat the same amount of liquid water to 80 °C ! Thus, almost any amount of excess summer heat over an extent of sea ice will be absorbed in the process of melting surface ice ice rather than significantly raising surface or air temperatures, whereas in other seasons with ambient temperatures considerably below zero degrees, excess heat directly warms the ice, bringing it from the deep freeze closer to the melting point. Once the ice is gone, summer surface air and water temperatures will rise considerably.
As long as at least a thin layer of sea ice remains frozen through summer it will continue doing its job of reflecting a lot of excess solar energy back to outer space. However, once a substantial fraction of that ice cover has melted, all hell will break loose! Excess energy that went into melting ice without changing its temperature will heat up cold water fast. An open Arctic Ocean under 24-hour a day solar heating will absorb several to many times as much energy that could be delivered through the ice, to say nothing of the fact that the air temperature over the open ocean may end up being many degrees hotter because it is no longer being cooled by melting ice.
For example, over the last few years weather stations on or near the Arctic Ocean coastline in Siberia and Alaska have recorded temperatures above 30°. With no ice cover, nothing would stop those temperatures extending out over the ocean adding to the heat. Ending the sunny season with sea surface temperatures of 10 – 20° could well prevent ice from forming over winter….. A radical change between one year and the next that would undoubtedly cause a ‘regime shift‘ in the behavior of Earth’s climate system. Removal of the sharp temperature difference between polar and sub-polar air masses will probably cause the polar jet stream system to collapse – at least over summer – leading to lethally extreme and long-lasting weather events such as heat domes beyond anything seen to date.
Time for a break before it gets worse…
Cartoonists sometimes have the knack of expressing human foibles. Their few words about cliimate hoaxes may provide a bit of a break before the last bit of climate reality reality that we humans are the only thing left with the capacity to resolve.

The universal laws of nature and evolution are what they are irrespective of human desires and intents
Most of these laws relate to the interactions of heat energy and pressure on gases, their mutual solubilities (i.e., the degree to which they can mix together), changes of state from gas ⇌ liquid ⇌ solid, and their spectroscopic properties (i.e., relatively easily measurable details of how they absorb and emit different wavelengths of radiant energy as a function of temperature and pressures. These differ considerably among the important gases that generate weather (water vapor, CO2, methane). These three gases also are heavily involved in very different ways in various aspects of the metabolisms of living systems. Physical interactions of the gases were already well understood in the early 20th Century and their biological behaviors by the 1960s and 1970s. What they do in all possible circumstances is purely a function of the fundamental laws of physics and chemistry that are totally independent of any human beliefs, fears, and desires. In other words, we have to live (or die) with whatever laws of nature that the Universe provides.
This includes extreme weather that is mostly driven by energy released or consumed by water as it changes in temperature (the energy here is called ‘sensible heat‘ because we can actually feel the temperature changing) or changes its state from solid (ice), to liquid (water), to gas (water vapor). The changes between ice and liquid water, and liquid water and water vapor consume large amounts of energy, but do not change the temperature. In this case the energy being transferred is called ‘latent energy‘.
Either kind of energy will change the density/pressure of the liquid or gas transferring the energy, or conversely externally pressure changes will affect the energy content of the parcel of molecules being affected by the pressure. Wikipedia’s article on ‘Weather’ explains how these laws work to generate weather. The basic message I am trying to communicate here is that the more energy applied to parcel of atmosphere, the more extreme its weather will be….
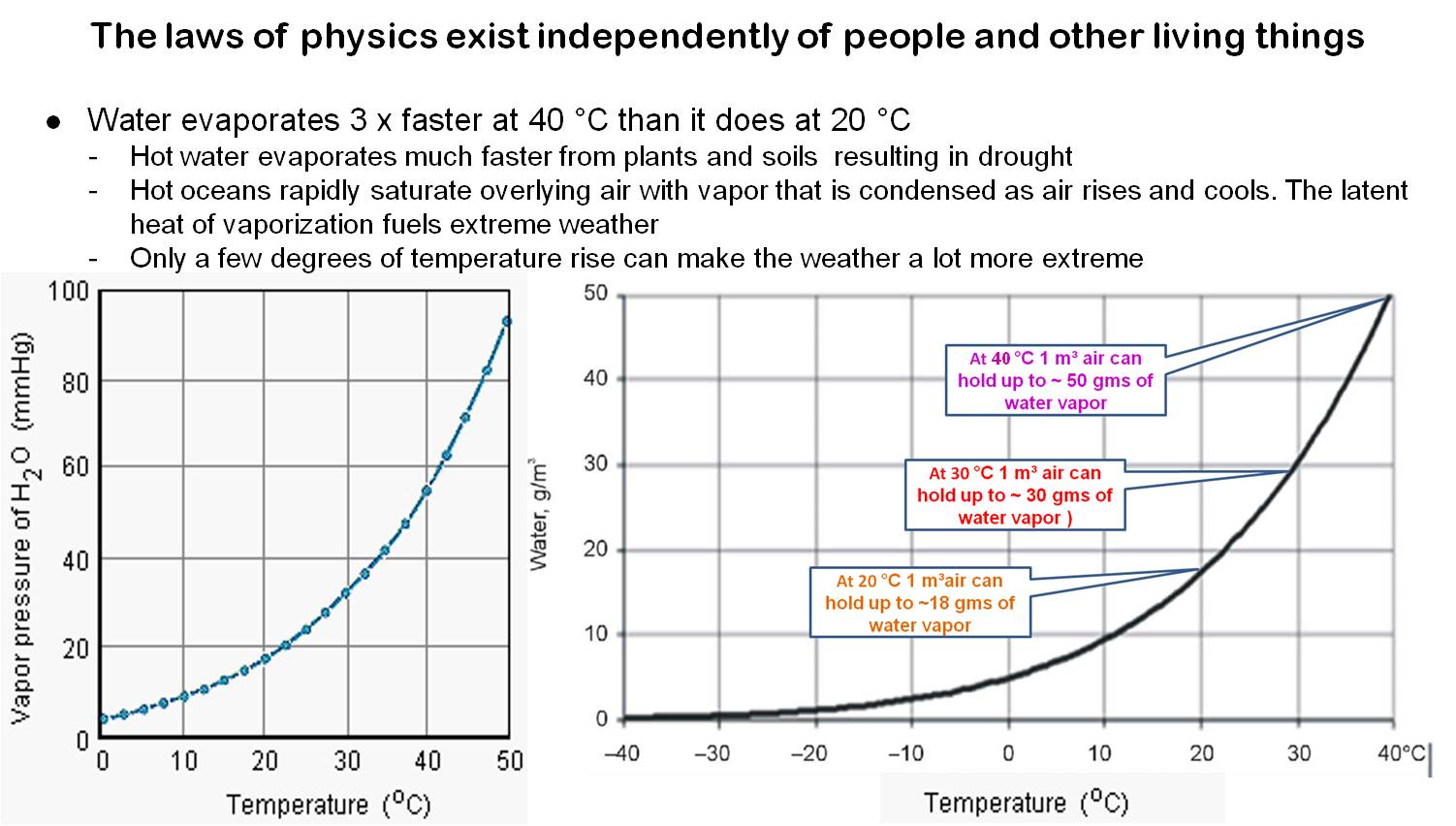
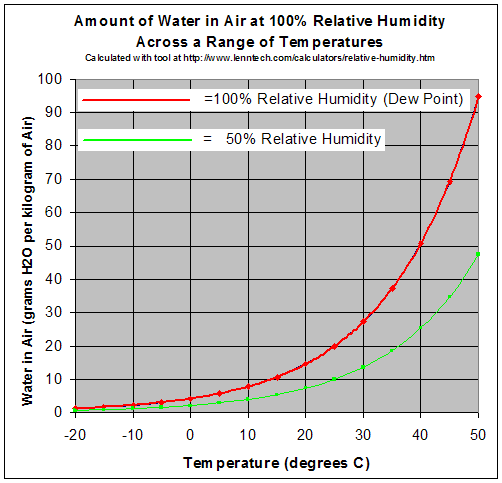
Some cases of extreme weather ramped up by increasing heat trapped by greenhouse gases
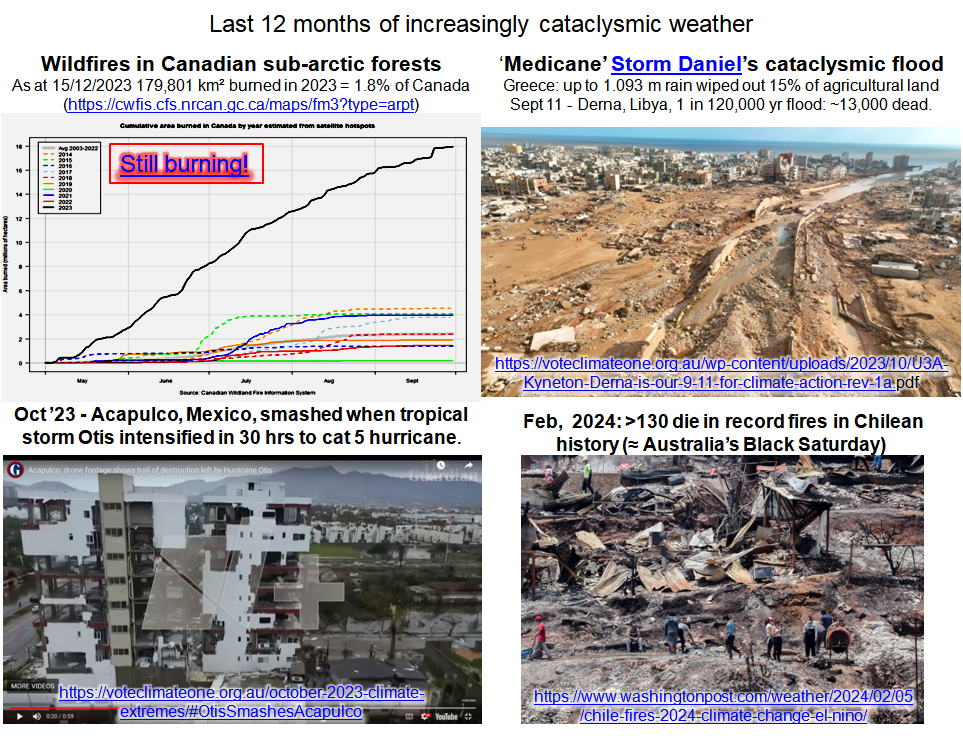
(1) Canada has a large proportion of the world’s subarctic/Boreal forests including a large area on carbon rich peaty soils on permafrost. For 20 years Canada has had a powerful satellite system for objectively tracking thee extent of wildfires. Record high temperatures and drought led to burning over 4x more area than than any of the past 20 years. The 2023 fires are estimated to have emitted 2.5 x times as much greenhouse gases as all sectors of the Canadian economy together. Some of the fires are still burning today in the peat soils and are already beginning to surface for the 2024 fire season (see also).
(2) on Sept. 10-11, 2023, a few days after dumping more than a meter of water on the north-eastern agricultural area of Greece, Storm Daniel dumped enough water on the Cyrenaican area of Libya to erase a major part of the high-rise center of the city of Derna, along with around 13,000 of the city’s inhabitants. (See Derna is our 9/11 for climate action for my initial survey of the event). I am still documenting details of the flooding from the comprehensive satellite, press, and social media imagery available, but it is clear from dateable geological evidence that this is the most extreme flood event along this area of coast since the Eemian period of the Last Interglacial ~120,000 years ago.
(3) Mexico’s major Pacific Coast resort city of Acapulco was comprehensively smashed by Cat 5 hurricane Otis. According to the US National Hurricane Center, Otis was the strongest hurricane in the Eastern Pacific to make landfall in the satellite era, and the second most rapidly intensifying hurricane in the recent era (US NOAA – National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service; unbelievable videos).
(4) Chile’s heatwaves and firestorms in early February are unprecedented and have killed more than 100 people.
Conclusion
The observations above point to the conclusion that we have already entered a new climate regime of positive feedbacks that are forcing Earth’s Climate System into the Hothouse Earth mode and a 6th global mass extinction event at least comparable to what caused the End Permian global mass extinction – only very much faster
Dynamical physical processes driven by positive feedbacks tend to grow exponentially until the process runs out of fuel or the system they are part of breaks. Humanity’s experiment to turn a significant percentage of Planet Earth’s fossil carbon (accumulated in the geosphere over hundreds of millions of years) into greenhouse gases in the atmosphere in a little more than a century is completely unprecedented in Earth’s history.
If humans cannot quickly reverse the feedbacks in global warming processes documented in this essay that have been triggered by our burning of a significant fraction of Earths fossil carbon driven, we’ll soon be extinct along with most other large, complex organisms currently inhabiting our single planet.
Bill McGuire, professor emeritus of geophysical & climate hazards at University College London and author of “Hothouse Earth: An Inhabitant’s Guide”, acknowledges this:
If the fracturing of our once stable climate doesn’t terrify you, then you don’t fully understand it. The reality is that, as far as we know, and in the natural course of events, our world has never — in its entire history — heated up as rapidly as it is doing now. Nor have greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere ever seen such a precipitous hike.
Think about that for a moment. We’re experiencing, in our lifetimes, a heating episode that is probably unique in the last 4.6 billion years.
…[T]his is a problem — a big one. After all, we can’t act effectively to tackle a crisis if we don’t know its full depth and extent.
…
What’s happening to our world scares the hell out of me, but if I shout the brutal, unvarnished truth from the rooftops, will this really galvanize you and others into fighting for the planet and your children’s futures? Or will it leave you frozen like a rabbit in headlights, convinced that all is lost? It is an absolutely critical question. With politicians and corporations unable or unwilling to take action rapidly enough to stymie emissions as the science demands, all we as climate scientists are left with is to seek to rouse the public to try and force through — via the ballot box and consumer choices — the enormous changes required to curb global heating.
Read the complete article: Bill McGuire, 7 Mar 2024, CNN. “Opinion: I’m a climate scientist. If you knew what I know, you’d be terrified too”
Most people find it difficult to think about the possible near-term end of our green living biosphere as we know it and extinction of the human species that depends on this biosphere for its survival. Many prefer to deny the reality of this possibility and continue with business as usual in the blind hope that nothing will change, than take it seriously and try to do something to avoid the extinction that we are still driving towards.
True, no individual action on its own can stop the planetary climate system from doing whatever it is going to do. But, the collective action of millions or even billions of humans mobilized and working together to use the best of our knowledge and technologies may still be able to alter this fatal path enough to reach some kind of sustainable future.
What gives me hope that we can solve the crisis…
is that even thoughtless greedy humans, starting ~200 years ago, had the demonstrated capacity to turn the planetary climate system onto its currently lethal trajectory.
The unplanned planetary geoengineering project to strengthen Earth’s greenhouse layer was driven by greedy men competing for power. It was begun by men wielding picks and shovels to mine fossil carbon, build canals, roads and rail, and men with poles and horses pulling wagons and barge loads of fossil carbon to fuel 18th Century steam powered technology. Much of the energy released from the carbon along with greenhouse gases was used by men to build increasingly sophisticated and powerful technology to dig up and burn ever more carbon faster and faster to fuel even more GHG emissions that are still increasing today.
Unlike our great, great, … grandparents, today’s instantly networked humans (women included!) have virtually instant Web access to the exponentially growing and collected knowledge of our history and increasingly powerful technologies and sciences. Is it not plausible that we now have the capacity to use the essentially unlimited resources of solar energy to reduce, remove, and repair enough of our past damage to Earth’s climate to find a way off the road to Hothouse Hell to a sustainable future?
As is blindingly obvious from the range of current measurements reported here of many different aspects of our global climate system it is clear average temperatures have risen so high and so much extra heat energy (both sensible and latent) has already been absorbed into the system that several temperature-related feedbacks have been pushed past thresholds where Earth’s natural processes will continue to force temperatures and GHG concentrations higher even if human GHG emissions stopped today.
As long as Earth’s energy imbalance continues to rise, global temperatures will also continue to rise as our planet tries to balance the books by radiating more energy at higher temperatures. Many animal species (including humans) and plants are already living close to the maximum temperatures their physiologies can survive. Local extinctions of populations are already happening every day – and when the last populations of a species dies off they can no longer (ever!) provide ecosystem services many other species cannot live without who could survive the ambient temperature. People can air-condition their living spaces, but they cannot survive the collapse of the agricultural ecosystem that provides the food we must eat in order to live.
Greedy stupid humans accidentally geoengineered the freeway to Earth’s Hothouse Hell and the Sixth Global Mass Extinction with the Industrial Revolution
This gives me a real hope that today’s wiser and more conscientious humans can geoengineer a greener road to a sustainable future.
Beginning very slowly in the mid 1700s, machine power began to replace human and animal muscle power for doing work to make and move things around in the environment. This began when it was discovered that the heat energy given off by combustion could be used to boil water to create steam in a pressure-tight container where the excess energy in the hot steam could be converted to mechanical work by driving a system of pistons, gears and connectors. In principal the steam engines could be fueled by burning wood, but the ancient forests were soon consumed by land clearing and agriculture. Coal was found to provide more energy per kilo than wood, but this had to be dug out of the ground and transported to where the power was needed.
Steam engines were first used to increase the rate of mining by allowing deeper areas to be mined. Gradually they replaced virtually every other source of mechanical power beyond the very limited areas that could be driven by falling water. Competition between nations and individuals for power in the broadest sense led to the positive feedbacks between the still rampant greed for power and the burning of fossil carbon in a wide variety of heat engines that is still increasing the rates of greenhouse gas emissions driving Earth’s Energy Imbalance to lethally high levels.
Human’s blind greed, starting with picks, shovels, and steam punk technology change ad whole planet’s life-giving atmosphere into a life-stifling heat blanket in less than 200 years. This fact screams out that with enough will, wisdom, foresight, and work that humans with our 21st Century knowledge of science, a vast array of technologies, and networking capabilities should be able to put the excess atmospheric carbon back into the ground. Although it may just still be possible for us to do this, it will not be easy. Greed and and the Second Law of Thermodynamics guarantee that. At the very least, it will involve a global mobilization on the scale of what Americans achieved in 1941 to win the Second World War (WWII). Two articles give small hints of what this actually involved: Social and economic changes – Encyclopedia.com, World War II Mobilization 1939-1943; and The Scientific and Technological Advances of World War II. (Note: the mobilization affected so many aspects of society, was so pervasive, and so rapid that I have been unable to find any single document that does justice to the revolutionary changes enacted by an initially divisive, isolationist, and hedonistic society not unlike Trumpist America is today.)
However, more than most people now alive, I am old enough to remember the end of WWII and the atom bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Thanks to the diverse threads in my lifetime of learning, I have come to understand that as a child I had first hand experience with the incredible total mobilization beginning in December 1939 and almost totally complete by the end of 1941; that won the War by 1945 through largely united social action informed by vast advances science and engineering. By 1941 the Axis powers (Germany, Japan and tag-along Italy) had controlled the whole of Europe between Great Britain and Moscow, virtually all of the Mediterranean border lands, the whole of East Asia save the western reaches of China and most of the Western Pacific save Australia and New Zealand. Within a little more than four more years, led by America, Germany and Japan were reduced to smoking rubble and unconditional surrenders. Within a few more years, the whole theater of war outside of Russian control was restored to functionality and even some degree of prosperity by the Marshal Plan for Europe and similar aid in Asia, initially under General Douglass MacArthur who had been Supreme Commander in the Pacific and oversaw the post-war occupation of Japan.
The brutal, unvarnished truth is that if record breaking climate trends established over the last year continue to accelerate as they have over this last year there’s a high likelihood that most species of large complex organisms, including humans, will be extinct before the end of the current 21st Century.
Most academic scientists, especially those reporting via the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) find it close to impossible to deal with the reality included within the socially and politically unacceptable term, ‘extinction’. Thus, to get the ‘brutal, unvarnished truth’ about what the facts the measurements of climate change are telling us that you need to know in order to prioritize your actions, you need to consider what retired curmudgeons like me have to say. Of course, you should also investigate whether they have qualifications that would give you reason to have the qualifications to actually understand what they are saying.
Nevertheless, the facts reported above show that we are already well started down the road to extinction and are rapidly running out of time when physics will transcend any conceivable actions humans might take to stop that progress. This was already apparent in 2022, even from the hyper-conservative IPCC’s publications, when UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres warned world leaders at COP 27 summit that nations must cooperate or face “collective suicide” from climate change because:
We are on a highway to Climate Hell – with our foot still on the accelerator!
UN Secretary General António Guterres at the Opening Ceremony of the World Leaders Summit | #COP27, 6 Nov 2022 – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YAVgd5XsvbE&t=130s… watch the entire speech.
The facts presented in this article show that in the ~16 months since COP27 the climate situation is far, far worse than almost anyone anticipated then. Yet, so far Guterres’s often repeated warnings that we were already accelerating towards “collective suicide” in [Earth’s] “Climate Hell” have been almost totally ignored by virtually all of the world’s nations, national medias, and most people.
Around the world virtually all nations and states are still practically owned by the self-interests who have the financial power to elect their puppets and useful idiots who work to protect the interests to national and state governments. Even in supposedly representative democracies like Australia, the USA, Great Britain, etc., they only need to control a few key representatives in parties forming majority governments…. Party discipline gives them control of the majority party, and thus government.
We must change the politics that has allowed this to happen and will prevent effective action that may for a small while yet allow humanity to climb back up over the cliff before we are cooked in the caldera of Hothouse Hell

To have any hope at all to organize and implement the kind of total mobilization that will be required to marshal the people, science, technology, and logistics to deal with the global emergency we must first revolutionize our governments to cut their allegiances with the industries that are killing us, either by changing the minds of our present representatives, or by replacing the puppets and useful idiots with progressive community independents who will act for the citizens who elect them by promoting, authorizing, and leading the kinds of actions required to address the emergency.
Vote Climate One along with Climate Rescue Accord and a number of other volunteer organizations have been formed to address the critical political issues, by identifying, promoting, advising, and electing suitable progressive and climate oriented candidates to our parliaments and governments who can be trusted to focus governments on mobilizing emergency actions to address the current existential emergency.
Footnotes:
- America’s mobilization for WWII shows what humans can do in an emergency situation if they work together.
I was born in 1939 and am old enough to actually remember the war’s ending: My father worked in the defence industry. We lived on a boat in the Port of Los Angeles close to the 2nd largest builder of Liberty Ships in the USA, and then in San Diego Harbor directly opposite North Island Naval Air Station and home port of the Pacific Fleet’s aircraft carriers. In my postgraduate career I worked for 15 months for the Atomic Energy Corporation; and for the last 17½ years prior to retirement I was a knowledge management systems analyst and designer in logistics support engineering for Tenix Defence (at the time, Australia’s largest defence engineering project manager). I have also read a lot of history, so I know a bit about what was mobilized and how it was done.
Until Dec 7 1941 when Japan bombed Pearl Harbor, Americans were isolationist deniers of the reality of Axis aggression (not unlike Trumpist ‘MAGA’). By 8 May 1945 Germany had been expunged and on 6 Aug. 1945 the atomic bombing of Hiroshima (and then Nagasaki a few days later) overwhelmed Japan. In 1941 nuclear fission was a wacky idea proposed by some academics. In 4 years nuclear science was developed, the Manhattan Project was conceived, several different kinds of production infrastructure (Hanford, Oak Ridge Facility, Savanna River)(a bit after the War), Los Alamos, etc…) were designed and built, atom bombs were designed, built, tested, and used. In the area of engineering and logistics, an average of 5 highly capable destroyers were built each month for 32 months and an average of 3 Liberty Ships every 2 days between 1941 and 1945. were able to be assembled and launched each week. The United Nations was formed, etc.. Equally prodigious challenges were met in many other areas that completely changed world history. Yes, conscription, coercion, rationing, etc. was required – but the global challenge was met and the common danger vanquished….
Today, we have massively more knowledge and prowess than we did in the early 1940’s. Humans can do remarkable things if people and governments unite and work together to fight the common danger. There is no greater danger than the near term extinction of our entire species and most of the rest of Earth’s biosphere! ↩︎ - Leon Simons makes a good case that the abrupt rise in the imbalance is at least partially due to the sharp reduction of sulfur emissions from worldwide shipping. The smog emitted along with CO2 by the burning of especially sulfurous diesel bunker fuel in the voyages of hundreds of thousands of ships per year almost certainly reflected a portion of the incoming solar energy back to space before it had a chance to be absorbed into the ocean – especially in the highly trafficked North Atlantic. See https://twitter.com/LeonSimons8/status/1668612887949217792. Stopping the sulfur emissions would certainly allow more solar energy to impinge on the ocean. Nevertheless it is still likely that the bulk of the rising temperature is due to the the increase in absorbed energy caused by the also rapidly increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases. ↩︎
- Few people who don’t actually work with satellite remote sensing technologies or work with their data products since the early 1980s have any idea how comprehensively weather, oceanographic and climatological variables are measured over space and time. Hundreds of operational satellites in polar orbits and dozens in geostationary orbits collect and send tens of millions of individual observations every day to government and private supercomputer centers on the ground for cross checking, validation and processing. Such centers are operated by the USA, EU, Russia, Japan, China, Australia, along with several university and commercial centers in the USA and EU — all competing to provide their customers with the most accurate information possible. In fact, so much information is available that in a couple hours of searching I have been unable to find any single reference to site here that comes close to providing a reasonable overview of the complete scope and depth of the available remote sensing data from satellites. ↩︎