Rising sea-level risk: can’t know when or how much
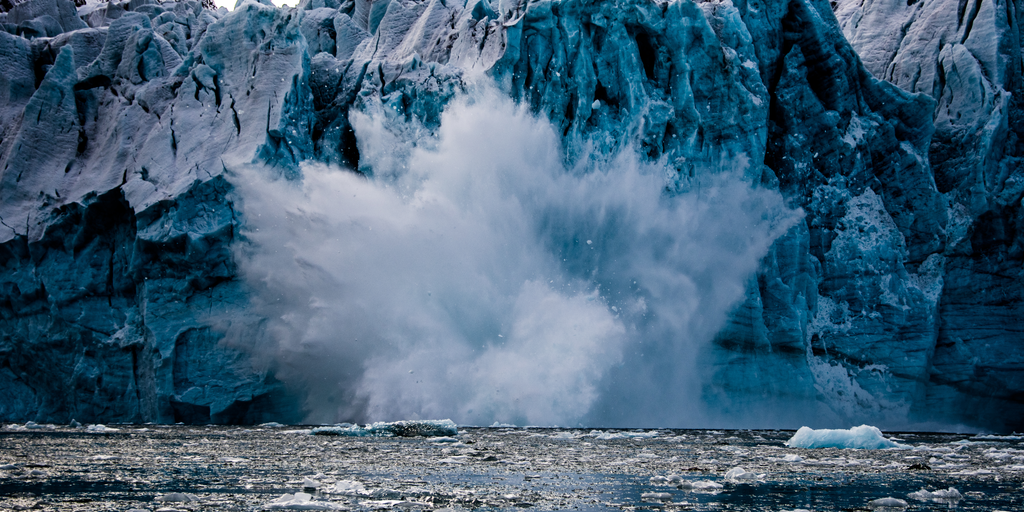

Melting polar glaciers are main contributors to rising sea level. The melting process is highly non-linear and thus inherently unpredictable
At least since the 1800s, world sea levels have been rising gradually but at a slowly accelerating rate. Since in the last 140 years it has risen around 17 cm, with around 6 cm of that in the 20 years between 2000 and 2020. And this is only a small part of the hugely complex planetary climate system that has an inherently unpredictable capacity to produce abrupt and catastrophically large changes in climate conditions.
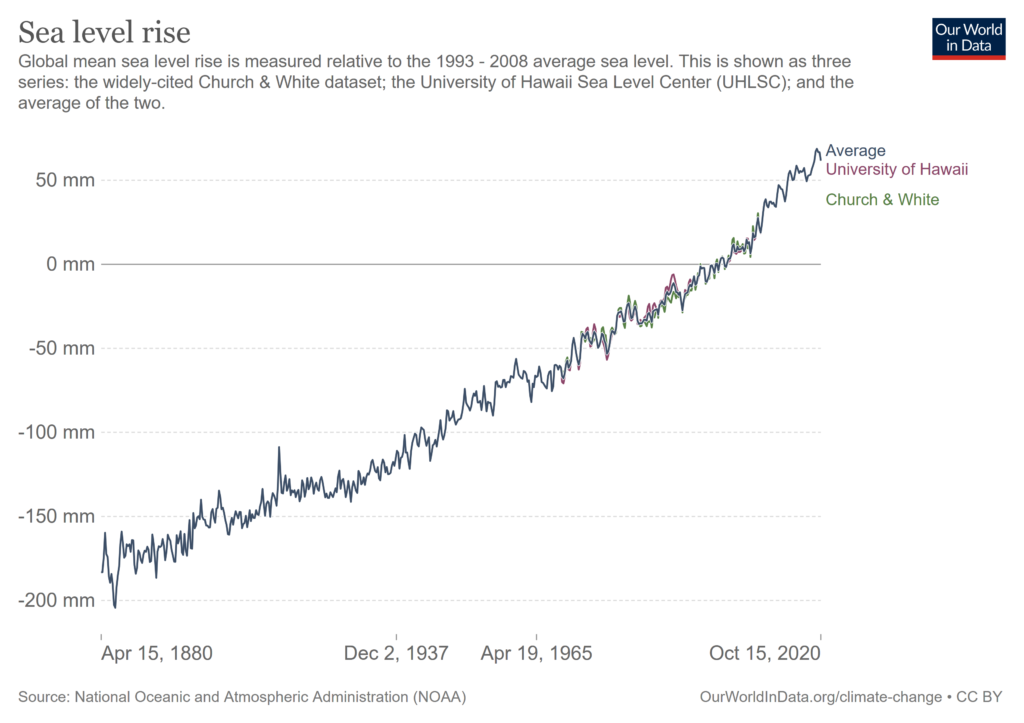
The rising sea-level has two sources: runoff from the land (mostly glacial melt water) and thermal expansion of the ocean itself due to warming from excess solar energy accumulating from the global warming process.
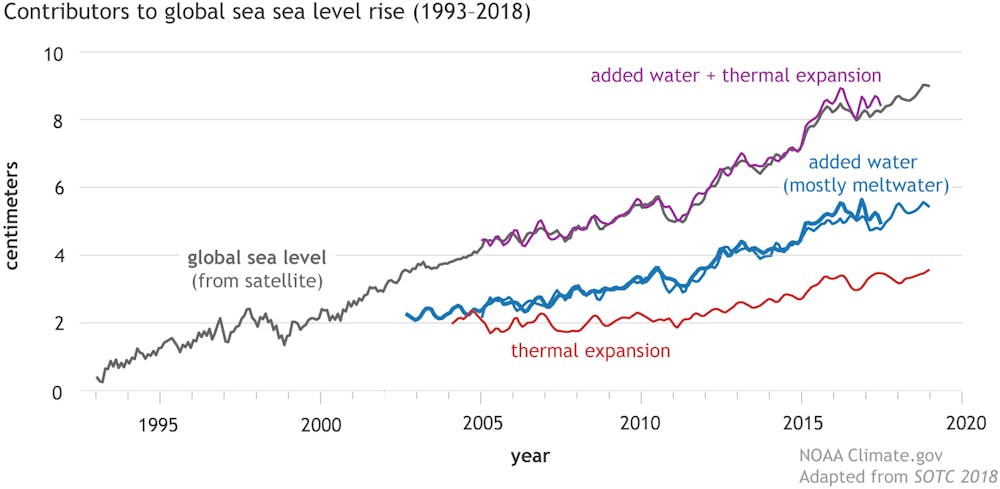
The melt water in the rising sea-level comes from two primary sources, melting glaciers and ice cap on Greenland that has increased 6-fold over the last couple of decades; and melting glaciers and ice cap on Antarctica which has more than doubled over the same time. This is measured by the loss of mass variable – representing the weight of the water that has been added to the oceans.
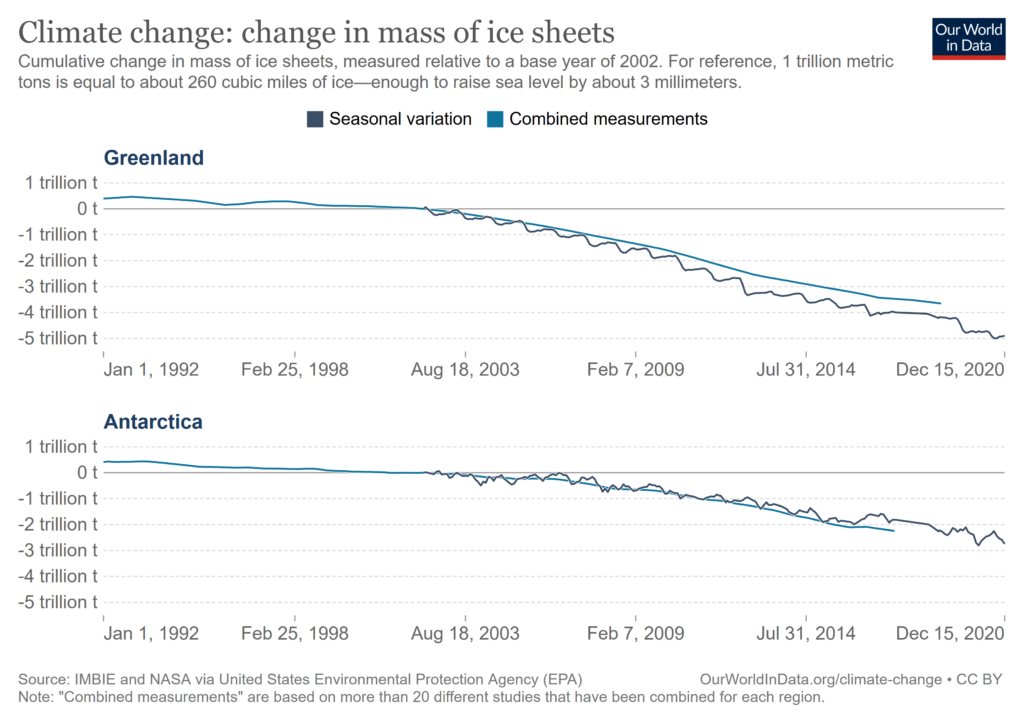
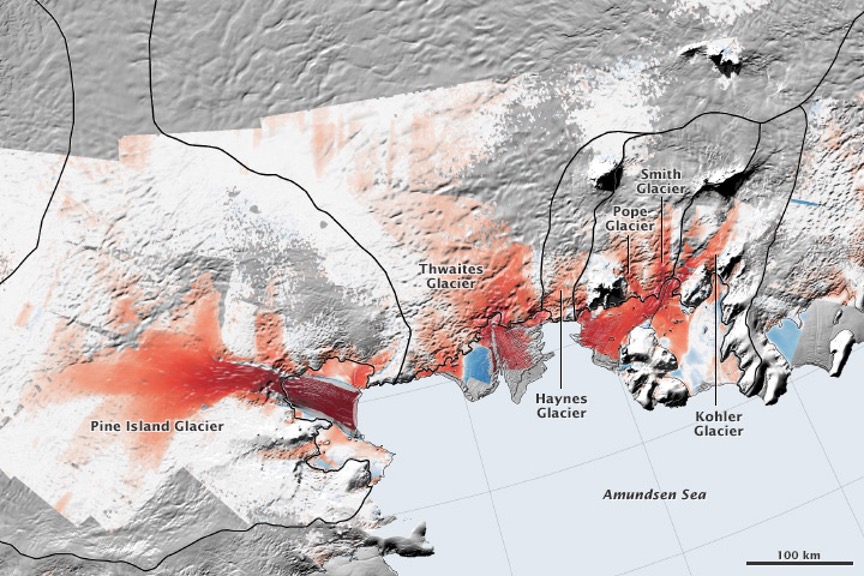
As described in the feature article below, the melting rate of a glacier is determined by its speed as it is creeping/sliding down the continental slope into the ocean. This in turn is determined by a complex set of interacting factors, e.g., temperature, angle of slope, width and roughness of the bed, how much meltwater is in the bed to lubricate/float the ice, where and how the ice may crack and crumble, how many bends there are in the valley, ocean conditions at the foot, whether and to what extent warm and salty (salt lowers the melting temperature of ice) ocean water penetrates into the glacier bed under its foot, thickness and extent of the floating ice shelf at the glacier’s foot and so on. Simply stated, melt rates are inherently unpredictable. However, one thing we can be sure of is that the melt rate will speed up as ambient temperatures increase the rate of ice melting, and rain replaces snow as the main form of precipitation.
The geological record provides good evidence that episodes of abrupt ice melting can cause raise sea-levels a lot faster than they are now, perhaps even showing large changes in rate over a few decades.
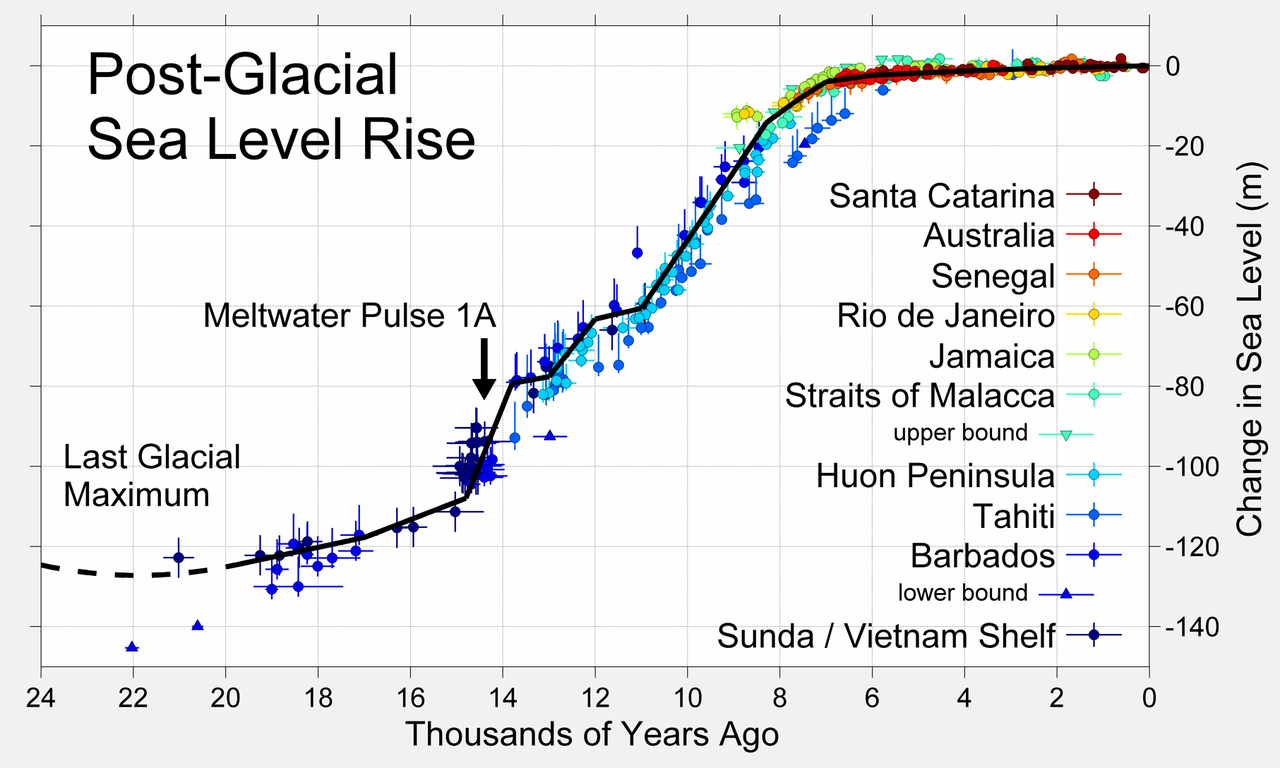
There may well be enough ice in the West Antarctic Ice Sheet — especially if combined with an equally rapid melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet to support an equivalent amount of melting to the Meltwater Pulse 1A. It is notable that the land surface underlying very large areas of both West Antarctica and Greenland are below sea level – giving ample opportunities for warm ocean water to help speed the melting and collapse of the ice sheets.

Why Melting Ice in Antarctica is Making Waves: Scientists recently discovered that the Thwaites Ice Shelf, a floating ice shelf that supports the Florida-sized Thwaites Glacier, could collapse in as little as five years because of global warming.
Climate Reality Project, 28/01/2022
This past December, the massive Thwaites Glacier in Western Antarctica made headlines for all the wrong reasons. Specifically, because new research revealed that the ice shelf preventing it from sliding into the ocean and drastically raising sea levels could collapse well within the next decade.
This Florida-sized glacier had already worried experts for years, going as far as to regularly be called the “Doomsday Glacier”. And yet, this update from the scientific community was still groundbreaking.
It’s news that the world — particularly low-lying island and coastal communities — should understand and act on. So, what exactly is Thwaites Glacier, what does the latest research about it say, and what consequences could come from its decline?
FIRST THINGS FIRST, WHAT IS THWAITES GLACIER?
Thwaites Glacier is a massive body of dense ice located in Western Antarctica. Measuring about 80 miles (120 km) across, it’s the widest glacier on Earth.
Thwaites Glacier in Western Antarctica. Credit: NASA
The glacier has an ice shelf — a permanent piece of floating ice connected to it — that branches out into the Amundsen Sea. Now, understanding what exactly an ice shelf does is crucial.
Read the complete article….
As long as the world continues to warm and large amounts of snow and ice remain lying on the land, sea levels will continue to rise. The risk of an abrupt sea-level rise is real. The human and economic costs of such an event would be catastrophic if it happens. It therefore makes very good sense that mitigation works should begin soon with planning in place at federal, state and local levels to accelerate the work if we have any clear early warning signs that abrupt melting is actually beginning.
It is also clear that our present LNP COALition governments deeply deny the risks Australia faces from global warming and the climate emergency, and should be replaced with rational people who put action on the climate emergency at the top of their to do lists if they should be elected to Parliament.

Also, from the official transcript dated 20/12/2019 from the PM’s own office, Scotty made it abundantly clear to John Stanley on 2GB Radio that HE doesn’t fight fires… “But I know Australians understand… that, you know, I don’t hold a hose, mate, and I don’t sit in a control room. That’s the brave people who do that are doing that job. But I know that Australians would want me back at this time out of these fatalities. So I’ll happily come back [from his secret holiday in Hawaii] and do that.”
Sixteen year-old Greta tells us and everyone at the 2019 World Economic Forum in Davos how we and our governments should actually respond to the climate emergency:

In other words, smell the smoke, see the reality, and fight the fire that is burning up our only planet so we can give our offspring a hopeful future. This is the only issue that matters. All Capt. Humbug and his troop of wooden-headed puppets are doing is rearranging the furniture in the burning house to be incinerated along with anything else we may care about. In Greta’s words, “even a small child can understand [this]”. People hope for their children’s futures. She doesn’t want your hope. She wants you to panic enough to wake up and fight the fire…. so she can have some hope for her future. Vote Climate One’s Traffic Light Voting System will help you use your vote wisely on behalf of our offsprings’ futures.
