True grimness of IPCC’s report still misunderstood
Most media concluded that emissions could go on rising until 2025 and the world could still stay under 1.5C. A potentially lethal error.

by Matt McGrath, 16/03/2022 in BBC News
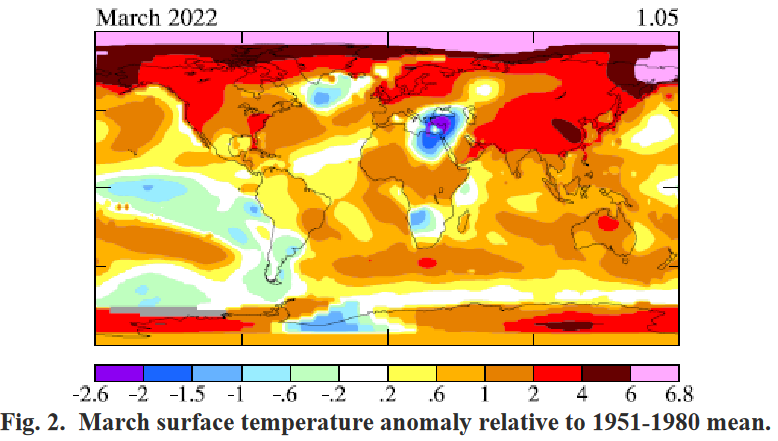
Climate change: Key UN finding widely misinterpreted: A key finding in the latest IPCC climate report has been widely misinterpreted, according to scientists involved in the study:
A major challenge in communicating complex messages about climate change is that the more simplified media reports of these events often have more influence than the science itself.
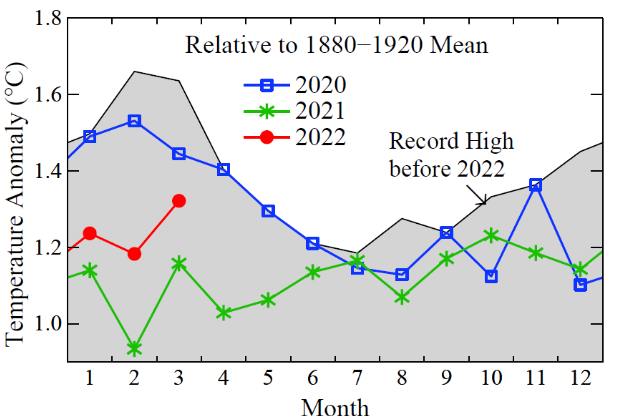
This worries observers who argue that giving countries the impression that emissions can continue to grow until 2025 would be a disaster for the world.
“We definitely don’t have the luxury of letting emissions grow for yet another three years,” said Kaisa Kosonen from Greenpeace.
“We have eight years to nearly halve global emissions. That’s an enormous task, but still doable, as the IPCC has just reminded us – but if people now start chasing emissions peak by 2025 as some kind of benchmark, we don’t have a chance.”
Read the complete article….
Editor’s note: Based on my rigorous evaluation of the IPCC’s scientific methodology and writing processes, even the corrected understanding of the IPCC report STILL UNDERSTATES the likelihood of the risk from, and the magnitude of consequences of failures or even delays in stopping the progress of global warming. In reality, the report says it is already too late to avoid global average temperatures rising more than 1.5 °C. By reaching net zero in 2030 AND extracting and sequestering most of the excess CO₂ already in the atmosphere we might be able to bring temperatures back down to 1.5 °C or less. Continuing with business as usual keeps us on the road to runaway warming to Earth’s Hothouse Hell and social collapse leading towards global mass extinction of humans and most other large and complex organisms on the planet.
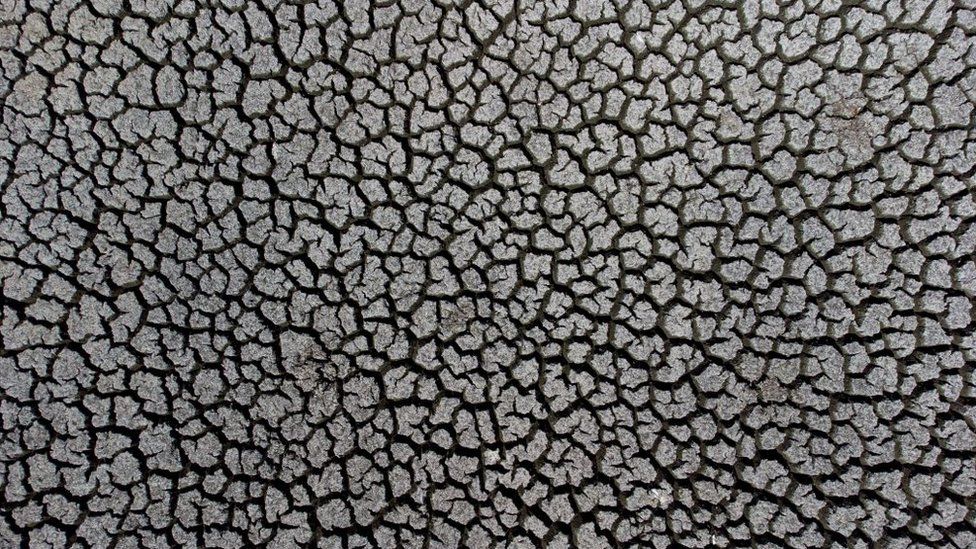
Featured Image: A dried out reservoir in Chile where drought has forced the government to take emergency measures. / Getty Images / from the article.