Floods and then more floods! Can we expect more yet?
Multiple floods in La Niña years are not unknown in Australia, but global warming can supply more water that makes extreme flooding even worse.

by Margaret Cook, 31/03/2022 in the Conversation
Why can floods like those in the Northern Rivers come in clusters?
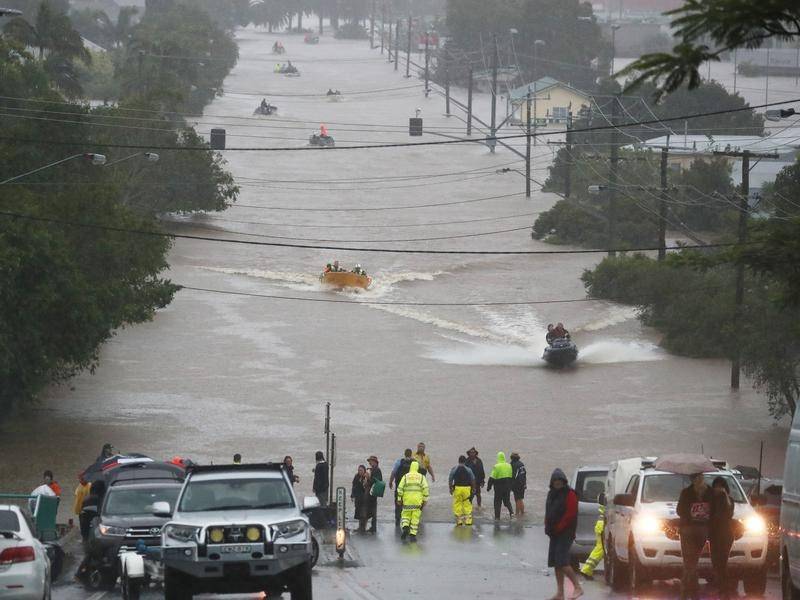
Right now, Lismore residents are going through their second major flood in a month.
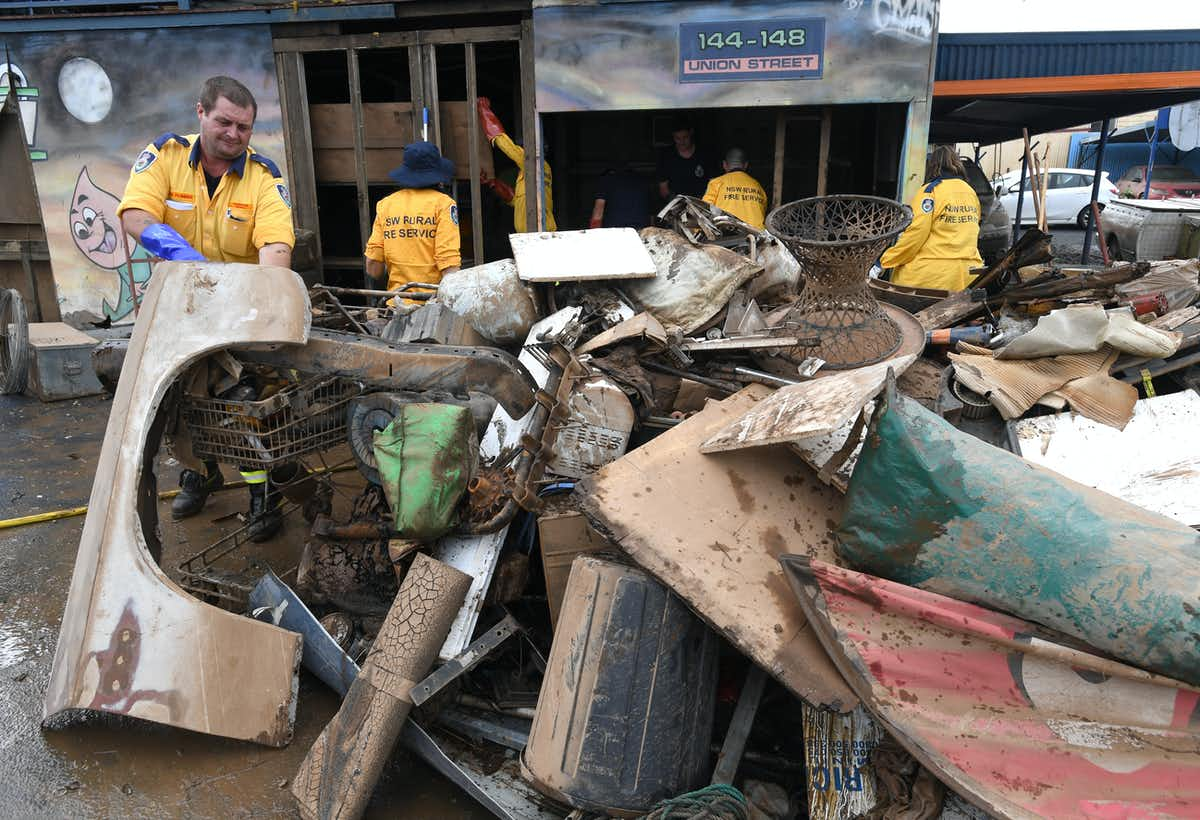
On February 28th, the devastating first flood peaked at 14.4 metres, fully two metres higher than the previous record of 12.27 metres in 1954, and well above the town’s 10-metre-high levee wall, constructed in 2005. Four people died, with 2000 homes destroyed or unlivable of the city’s 19,000.
Even as Lismore and Northern Rivers residents struggle to recover from the first flood, the floods are coming again. On March 29th, more heavy rain began falling onto the soaked catchment feeding into Wilsons River.
Read the complete article….
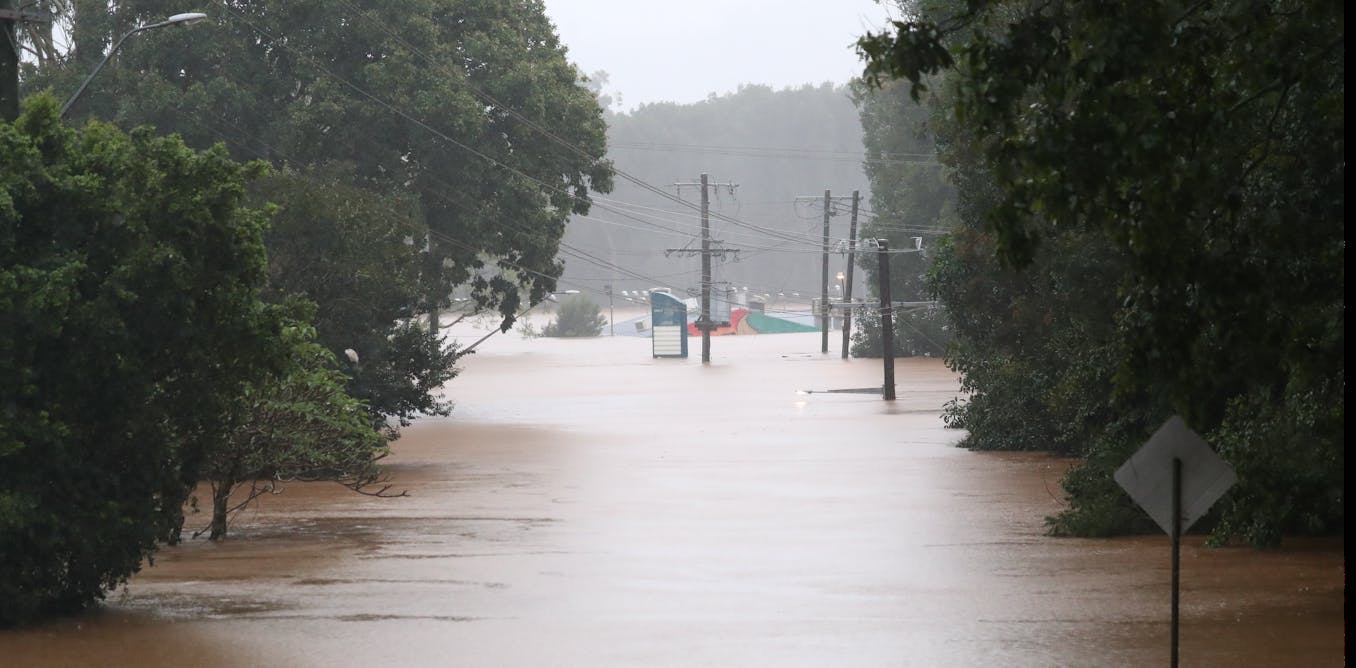
Featured Image: Lismore locals are still cleaning up after February’s floods – now they are being hit again. Darren England/AAP Image / from the article.